Atmospheric Nonthermal Plasma-Treated PBS Inactivates Escherichia coli by Oxidative DNA Damage
- PMID: 26461113
- PMCID: PMC4603800
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0139903
Atmospheric Nonthermal Plasma-Treated PBS Inactivates Escherichia coli by Oxidative DNA Damage
Abstract
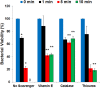
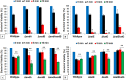
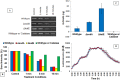
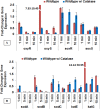
We recently reported that phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) treated with nonthermal dielectric-barrier discharge plasma (plasma) acquires strong antimicrobial properties, but the mechanisms underlying bacterial inactivation were not known. The goal of this study is to understand the cellular responses of Escherichia coli and to investigate the properties of plasma-activated PBS. The plasma-activated PBS induces severe oxidative stress in E. coli cells and reactive-oxygen species scavengers, α-tocopherol and catalase, protect E. coli from cell death. Here we show that the response of E. coli to plasma-activated PBS is regulated by OxyR and SoxyRS regulons, and mediated predominantly through the expression of katG that deactivates plasma-generated oxidants. During compensation of E. coli in the absence of both katG and katE, sodA and sodB are significantly overexpressed in samples exposed to plasma-treated PBS. Microarray analysis found that up-regulation of genes involved in DNA repair, and E. coli expressing recA::lux fusion was extremely sensitive to the SOS response upon exposure to plasma-treated PBS. The cellular changes include rapid loss of E. coli membrane potential and membrane integrity, lipid peroxidation, accumulation of 8-hydroxy-deoxyguinosine (8OHdG), and severe oxidative DNA damage; reveal ultimate DNA disintegration, and cell death. Together, these data suggest that plasma-treated PBS contains hydrogen peroxide and superoxide like reactive species or/and their products which lead to oxidative changes to cell components, and are eventually responsible for cell death.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Escherichia coli cellular responses to exposure to atmospheric-pressure dielectric barrier discharge plasma-treated N-acetylcysteine solution.J Appl Microbiol. 2018 Aug;125(2):383-397. doi: 10.1111/jam.13777. Epub 2018 May 4. J Appl Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29624820
-
Mutagenesis and stress responses induced in Escherichia coli by hydrogen peroxide.J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):2967-76. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.2967-2976.1987. J Bacteriol. 1987. PMID: 3298208 Free PMC article.
-
Morphology analysis of Escherichia coli treated with nonthermal plasma.J Appl Microbiol. 2017 Jan;122(1):87-96. doi: 10.1111/jam.13335. J Appl Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 27792254
-
Regulators of oxidative stress response genes in Escherichia coli and their functional conservation in bacteria.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2012 Sep 15;525(2):161-9. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2012.02.007. Epub 2012 Feb 20. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2012. PMID: 22381957 Review.
-
Genetic mechanisms involved in cellular recovery from oxidative stress.Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 1995;29(2):159-73. doi: 10.1002/arch.940290206. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 1995. PMID: 7606042 Review.
Cited by
-
Oxidative lesions and post-treatment viability attenuation of listeria monocytogenes triggered by atmospheric non-thermal plasma.J Appl Microbiol. 2022 Oct;133(4):2348-2360. doi: 10.1111/jam.15688. Epub 2022 Aug 3. J Appl Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35751464 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of multiple stressors induced by non-thermal plasma-charged aerosols during inactivation of airborne bacteria.PLoS One. 2017 Feb 6;12(2):e0171434. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0171434. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28166240 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of Clinically Important Bacteria With Cold Atmospheric Plasma.Microb Biotechnol. 2025 Aug;18(8):e70219. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.70219. Microb Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40831155 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effect of Urinary Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Metabolites on Lipid Profiles: Does Oxidative Stress Play a Crucial Mediation Role?Toxics. 2024 Oct 15;12(10):748. doi: 10.3390/toxics12100748. Toxics. 2024. PMID: 39453168 Free PMC article.
-
Toxicity Assessment of Long-Term Exposure to Non-Thermal Plasma Activated Water in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 26;22(21):11534. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111534. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34768973 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Storz G, Imlay JA. Oxidative stress. Current opinion in microbiology. 1999;2(2):188–94. Epub 1999/05/14. . - PubMed
-
- Joshi SG, Cooper M, Yost A, Paff M, Ercan UK, Fridman G, et al. Nonthermal dielectric-barrier discharge plasma-induced inactivation involves oxidative DNA damage and membrane lipid peroxidation in Escherichia coli. Antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy. 2011;55(3):1053–62. Epub 2011/01/05. 10.1128/AAC.01002-10 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yoon SJ, Park JE, Yang JH, Park JW. OxyR regulon controls lipid peroxidation-mediated oxidative stress in Escherichia coli. Journal of biochemistry and molecular biology. 2002;35(3):297–301. Epub 2002/09/26. . - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

