The prognostic value of peripheral CD4+CD25+ T lymphocytes among early stage and triple negative breast cancer patients receiving dendritic cells-cytokine induced killer cells infusion
- PMID: 26462021
- PMCID: PMC4747410
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.5534
The prognostic value of peripheral CD4+CD25+ T lymphocytes among early stage and triple negative breast cancer patients receiving dendritic cells-cytokine induced killer cells infusion
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to assess the prognostic value of CD4+CD25+ T lymphocyte in peripheral blood among breast cancer patients treated with adoptive T lymphocytes immunotherapy.
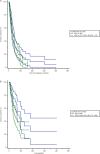
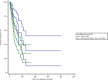
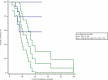
Methods: 217 patients participated in the follow-up study. CD4+CD25+ proportion was measured by flow cytometry in peripheral T cells. The median survival was estimated by Kaplan-Meier curve, Log-rank test and Cox hazard proportion regression model, between groups of CD4+CD25+ proportion more than 5% and less than or equal to 5% in peripheral T cells.
Results: Peripheral CD4+CD25+ T lymphocytes had not a relationship with progression-free survival. It was featured that above 5% peripheral CD4+CD25+ proportion of T cells was related with the median overall survival by a shorten of 51 months (p < 0.05) with the HR 1.65 (95%CI 1.04, 2.62). Above 5% CD4+CD25+proportion of T cells produced the HR to be 1.76 (95%CI 1.07, 2.87) In stage 0-II patients, and 3.59 (95%CI 1.05, 12.29) in triple negative breast cancer patients.
Conclusions: Cellular immunity restoration recovered by adoptive T cell infusions which resulted in less proportion of peripheral CD4+CD25+T lymphocytes could be a potential prognostic indicator among early stage and triple negative patients.
Keywords: CD4+CD25+ T lymphocyte; adoptive cell therapy; early stage breast cancer; prognosis; triple negative breast cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
There are none.
Figures
References
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Ervik M, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin D, Forman D, Bray F. GLOBOCAN 2012 v1.0, Cancer Incidence and Mortality Worldwide: IARC CancerBase No. 11 [Internet] Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2013. Available from: http://globocan.iarc.fr, accessed on 26/01/2015.
-
- Choudhury A, Palma M, Mellstedt H. The future of cancer vaccines for non-small-cell lung cancer: ongoing trials. Clinical lung cancer. 2008;1:S37–44. - PubMed
-
- Joshi PS, Liu JQ, Wang Y, Chang X, Richards J, Assarsson E, Shi FD, Ljunggren HG, Bai XF. Cytokine-induced killer T cells kill immature dendritic cells by TCR-independent and perforin-dependent mechanisms. Journal of leukocyte biology. 2006;80:1345–1353. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

