Inhibiting bladder tumor growth with a cell penetrating R11 peptide derived from the p53 C-terminus
- PMID: 26462022
- PMCID: PMC4741965
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.5622
Inhibiting bladder tumor growth with a cell penetrating R11 peptide derived from the p53 C-terminus
Abstract
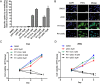
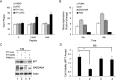
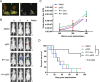
Urothelial carcinoma of the bladder (UCB) is the most common malignancy of the urinary tract, nearly half of which contains a mutation in TP53 gene. Hence, therapeutic approach by restoring functional p53 protein in cancer cells will be beneficial. Recent studies have demonstrated the inhibition of cancer cell growth by p53 reactivation using a peptide derived from the p53 C-terminus (p53C). However, the outcome of reactivating p53 in controlling bladder cancer development is limited by its efficiency and specificity of peptide delivery, especially in metastatic animal models. Herein, we report that the cell penetrating peptide (polyarginine, R11)-conjugated p53C can exhibit a preferential uptake and growth inhibit of UCB cells expressing either mutant or wild-type TP53 by the activation of p53-dependent pathway. R11-p53C peptide treatment of preclinical orthotopic and metastatic bladder cancer models significantly decreased the tumor burden and increased the lifespan without a significant cytotoxicity. Based on these results, we believe that R11-p53C peptide has therapeutic potential for primary and metastatic bladder cancer, and R11-mediated transduction may be a useful strategy for the therapeutic delivery of large tumor suppressor molecules to tumor cells in vitro and in vivo.
Keywords: bladder cancer; cell penetrating peptide; metastatic tumor; p53 C-terminus; targeted therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-155 promotes bladder cancer growth by repressing the tumor suppressor DMTF1.Oncotarget. 2015 Jun 30;6(18):16043-58. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3755. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25965824 Free PMC article.
-
Reactivation of wild-type and mutant p53 by tryptophanolderived oxazoloisoindolinone SLMP53-1, a novel anticancer small-molecule.Oncotarget. 2016 Jan 26;7(4):4326-43. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6775. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26735173 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-penetrating D-isomer peptides of p53 C-terminus: long-term inhibitory effect on the growth of bladder cancer.Urology. 2010 Apr;75(4):813-9. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2009.10.002. Epub 2009 Dec 6. Urology. 2010. PMID: 19963248
-
Gene products involved in metastasis of bladder cancer.Histol Histopathol. 2003 Jul;18(3):969-80. doi: 10.14670/HH-18.969. Histol Histopathol. 2003. PMID: 12792907 Review.
-
A critical analysis of the use of p53 as a marker for management of bladder cancer.Urol Clin North Am. 2000 Feb;27(1):75-82, ix. doi: 10.1016/s0094-0143(05)70236-6. Urol Clin North Am. 2000. PMID: 10696247 Review.
Cited by
-
Biological Properties of Arginine-rich Peptides and their Application in Cargo Delivery to Cancer.Curr Drug Deliv. 2025;22(4):387-400. doi: 10.2174/1567201820666230417083350. Curr Drug Deliv. 2025. PMID: 37073158 Review.
-
DDR2 overexpression in urothelial carcinoma indicates an unfavorable prognosis: a large cohort study.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 29;7(48):78918-78931. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12912. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27793038 Free PMC article.
-
Cell Penetrating Peptides, Novel Vectors for Gene Therapy.Pharmaceutics. 2020 Mar 3;12(3):225. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12030225. Pharmaceutics. 2020. PMID: 32138146 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in Research on Bladder Cancer Targeting Peptides: a Review.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2021 Dec;79(4):711-718. doi: 10.1007/s12013-021-01019-3. Epub 2021 Sep 1. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2021. PMID: 34468956 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances of Cell-Penetrating Peptides and Their Application as Vectors for Delivery of Peptide and Protein-Based Cargo Molecules.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Aug 7;15(8):2093. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15082093. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37631307 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Stenzl A, Cowan NC, De Santis M, Kuczyk MA, Merseburger AS, Ribal MJ, Sherif A, Witjes JA. Treatment of muscle-invasive and metastatic bladder cancer: update of the EAU guidelines. Eur Urol. 2011;59:1009–1018. - PubMed
-
- Al-Sukhun S, Hussain M. Current understanding of the biology of advanced bladder cancer. Cancer. 2003;97:2064–2075. - PubMed
-
- Ko LJ, Prives C. p53: puzzle and paradigm. Genes Dev. 1996;10:1054–1072. - PubMed
-
- Selivanova G, Iotsova V, Okan I, Fritsche M, Strom M, Groner B, Grafstrom RC, Wiman KG. Restoration of the growth suppression function of mutant p53 by a synthetic peptide derived from the p53 C-terminal domain. Nat Med. 1997;3:632–638. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

