A Panel of Genetic Polymorphism for the Prediction of Prognosis in Patients with Early Stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer after Surgical Resection
- PMID: 26462029
- PMCID: PMC4603900
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140216
A Panel of Genetic Polymorphism for the Prediction of Prognosis in Patients with Early Stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer after Surgical Resection
Abstract
Background: This study was conducted to investigate whether a panel of eight genetic polymorphisms can predict the prognosis of patients with early stage non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) after surgical resection.
Materials and methods: We selected eight single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) which have been associated with the prognosis of lung cancer patients after surgery in our previous studies. A total of 814 patients with early stage NSCLC who underwent curative surgical resection were enrolled. The association of the eight SNPs with overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) was analyzed.
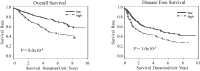
Results: The eight SNPs (CD3EAP rs967591, TNFRSF10B rs1047266, AKT1 rs3803300, C3 rs2287845, HOMER2 rs1256428, GNB2L1 rs3756585, ADAMTSL3 rs11259927, and CD3D rs3181259) were significantly associated with OS and/or DFS. Combining those eight SNPs, we designed a prognostic index to predict the prognosis of patients. According to relative risk of death, a score value was assigned to each genotype of the SNPs. A worse prognosis corresponded to a higher score value, and the sum of score values of eight SNPs defined the prognostic index of a patient. When we categorized the patients into two groups based on the prognostic index, high risk group was significantly associated with worse OS and DFS compared to low risk group (aHR for OS = 2.21, 95% CI = 1.69-2.88, P = 8.0 x 10-9, and aHR for DFS = 1.58, 95% CI = 1.29-1.94, P = 1.0 x 10-5).
Conclusions: Prognostic index using eight genetic polymorphisms may be useful for the prognostication of patients with surgically resected NSCLC.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Development of a prognosis-prediction model incorporating genetic polymorphism with pathologic stage in stage I non-small cell lung cancer: A multicenter study.Thorac Cancer. 2017 May;8(3):251-259. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.12434. Epub 2017 Mar 31. Thorac Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28371058 Free PMC article.
-
Association between genetic variants in pre-microRNAs and survival of early-stage NSCLC.J Thorac Oncol. 2013 Jun;8(6):703-10. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e318288dc0a. J Thorac Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23470291
-
Genetic polymorphisms in glycolytic pathway are associated with the prognosis of patients with early stage non-small cell lung cancer.Sci Rep. 2016 Oct 21;6:35603. doi: 10.1038/srep35603. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27767175 Free PMC article.
-
AKT1 polymorphisms and survival of early stage non-small cell lung cancer.J Surg Oncol. 2012 Feb;105(2):167-74. doi: 10.1002/jso.22071. Epub 2011 Aug 12. J Surg Oncol. 2012. PMID: 21842521
-
Sarcopenia is an independent unfavorable prognostic factor of non-small cell lung cancer after surgical resection: A comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Surg Oncol. 2019 May;45(5):728-735. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2018.09.026. Epub 2018 Oct 15. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30348603
Cited by
-
Analysis of Complement C3 Gene Reveals Susceptibility to Severe Preeclampsia.Front Immunol. 2017 May 29;8:589. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00589. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28611769 Free PMC article.
-
Akt1 genetic variants confer increased susceptibility to thyroid cancer.Endocr Connect. 2020 Nov;9(11):1065-1074. doi: 10.1530/EC-20-0311. Endocr Connect. 2020. PMID: 33112820 Free PMC article.
-
The Interplay between T Cells and Cancer: The Basis of Immunotherapy.Genes (Basel). 2023 Apr 28;14(5):1008. doi: 10.3390/genes14051008. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37239368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Naturally Occurring Genetic Alterations in Proximal TCR Signaling and Implications for Cancer Immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2021 May 3;12:658611. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.658611. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34012443 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic variations in the PI3K-PTEN-AKT-mTOR pathway are associated with distant metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients treated with intensity-modulated radiation therapy.Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 23;6:37576. doi: 10.1038/srep37576. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27876891 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ludwig JA, Weinstein JN. Biomarkers in cancer staging, prognosis and treatment selection. Nature reviews 2005;5:845–56. - PubMed
-
- Arriagada R, Bergman B, Dunant A, Le Chevalier T, Pignon JP, Vansteenkiste J. Cisplatin-based adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with completely resected non-small-cell lung cancer. The New England journal of medicine 2004;350:351–60. - PubMed
-
- Winton T, Livingston R, Johnson D, Rigas J, Johnston M, Butts C, et al. Vinorelbine plus cisplatin vs. observation in resected non-small-cell lung cancer. The New England journal of medicine 2005;352:2589–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous