Mitochondrial ATF2 translocation contributes to apoptosis induction and BRAF inhibitor resistance in melanoma through the interaction of Bim with VDAC1
- PMID: 26462148
- PMCID: PMC4742181
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.5537
Mitochondrial ATF2 translocation contributes to apoptosis induction and BRAF inhibitor resistance in melanoma through the interaction of Bim with VDAC1
Abstract
Background: The mitochondrial accumulation of ATF2 is involved in tumor suppressor activities via cytochrome c release in melanoma cells. However, the signaling pathways that connect mitochondrial ATF2 accumulation and cytochrome c release are not well documented.
Methods: Several melanoma cell lines, B16F10, K1735M2, A375 and A375-R1, were treated with paclitaxel and vemurafenib to test the function of mitochondrial ATF2 and its connection to Bim and voltage-dependent anion channel 1 (VDAC1). Immunoprecipitation analysis was performed to investigate the functional interaction between the involved proteins. VDAC1 oligomerization was evaluated using an EGS-based crosslinking assay.
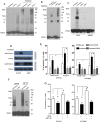
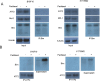
Results: The expression and migration of ATF2 to the mitochondria accounted for paclitaxel stimuli and acquired resistance to BRAF inhibitors. Mitochondrial ATF2 facilitated Bim stabilization through the inhibition of its degradation by the proteasome, thereby promoting cytochrome c release and inducing apoptosis in B16F10 and A375 cells. Studies using B16F10 and A375 cells genetically modified for ATF2 indicated that mitochondrial ATF2 was able to dissociate Bim from the Mcl-1/Bim complex to trigger VDAC1 oligomerization. Immunoprecipitation analysis revealed that Bim interacts with VDAC1, and this interaction was remarkably enhanced during apoptosis.
Conclusion: These results reveal that mitochondrial ATF2 is associated with the induction of apoptosis and BRAF inhibitor resistance through Bim activation, which might suggest potential novel therapies for the targeted induction of apoptosis in melanoma therapy.
Keywords: ATF2; Bim; Mcl-1; VDAC1; mitochondria.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article are reported.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Bim and VDAC1 are hierarchically essential for mitochondrial ATF2 mediated cell death.Cancer Cell Int. 2015 Mar 30;15:34. doi: 10.1186/s12935-015-0188-y. eCollection 2015. Cancer Cell Int. 2015. PMID: 25852302 Free PMC article.
-
The HSP90 inhibitor XL888 overcomes BRAF inhibitor resistance mediated through diverse mechanisms.Clin Cancer Res. 2012 May 1;18(9):2502-14. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-2612. Epub 2012 Feb 20. Clin Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22351686 Free PMC article.
-
RAF inhibition overcomes resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis in melanoma cells.J Invest Dermatol. 2014 Feb;134(2):430-440. doi: 10.1038/jid.2013.347. Epub 2013 Aug 16. J Invest Dermatol. 2014. PMID: 23955071
-
The mitochondrial voltage-dependent anion channel 1 in tumor cells.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Oct;1848(10 Pt B):2547-75. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2014.10.040. Epub 2014 Nov 4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25448878 Review.
-
Oligomerization of the mitochondrial protein VDAC1: from structure to function and cancer therapy.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2013;117:303-34. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-386931-9.00011-8. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2013. PMID: 23663973 Review.
Cited by
-
The activating transcription factor 2: an influencer of cancer progression.Mutagenesis. 2019 Dec 19;34(5-6):375-389. doi: 10.1093/mutage/gez041. Mutagenesis. 2019. PMID: 31799611 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perturbing mitosis for anti-cancer therapy: is cell death the only answer?EMBO Rep. 2018 Mar;19(3):e45440. doi: 10.15252/embr.201745440. Epub 2018 Feb 19. EMBO Rep. 2018. PMID: 29459486 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging roles of activating transcription factor 2 in the development of breast cancer: a comprehensive review.Precis Clin Med. 2023 Oct 25;6(4):pbad028. doi: 10.1093/pcmedi/pbad028. eCollection 2023 Dec. Precis Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37955015 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Membrane Transporters and Channels in Melanoma.Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2021;181:269-374. doi: 10.1007/112_2020_17. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 32737752 Review.
-
VDAC1, as a downstream molecule of MLKL, participates in OGD/R-induced necroptosis by inducing mitochondrial damage.Heliyon. 2023 Dec 11;10(1):e23426. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23426. eCollection 2024 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38173512 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

