Novel host genetic variations associated with spontaneous clearance of a single-source outbreak of HCV1b infections
- PMID: 26462265
- PMCID: PMC4533326
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjgast-2014-000010
Novel host genetic variations associated with spontaneous clearance of a single-source outbreak of HCV1b infections
Abstract
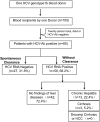
Background and aims: A total of 105 patients were identified as accidentally infected with hepatitis C virus genotype 1b (HCV1b) through blood transfusion from a single blood donor. This group provides a unique patient population to study host factors involved in the spontaneous clearance of HCV and disease progression.
Methods: Clinical markers, HCV RNA and eight single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of interleukin-28B (IL-28B) were detected. Exome capture and sequencing were analysed for association with HCV clearance.
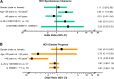
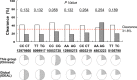
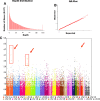
Results: Among the 85 patients with the positive HCV antibody, 27 cases (31.8%) were HCV RNA negative over a period of 9-12 years. Of the 58 patients with positive HCV RNA, 22.4% developed chronic hepatitis, and 5.2% developed cirrhosis. Age was found to be associated with HCV1b clearance. IL-28 rs10853728 CC showed the trend. By exon sequencing, 39 SNPs were found to be significantly different in spontaneous clearance patients (p<0.001). Two SNPs in the tenascin receptor (TNR), five in the transmembrane protease serine 11A (TMPRSS11A), and one in the serine peptidase inhibitor kunitz type 2 (SPINT2) showed the closest associations (p<10(-5)).
Conclusions: Host genetic analyses on the unique, single source HCV1b-infected patient population has suggested that age and mutations in TNR, TMPRSS11A and SPINT2 genes may be factors associated with HCV clearance.
Keywords: CHRONIC HEPATITIS; GENETICS; HCV.
Figures
References
-
- Seeff LB. Natural history of chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2002;36:S35–46. - PubMed
-
- Mosley JW, Operskalski EA, Tobler LH, et al. . Viral and host factors in early hepatitis C virus infection. Hepatology 2005;42:86–92. - PubMed
-
- Ge D, Fellay J, Thompson AJ, et al. . Genetic variation in IL28B predicts hepatitis C treatment-induced viral clearance. Nature 2009;461:399–401. - PubMed
-
- Suppiah V, Moldovan M, Ahlenstiel G, et al. . IL28B is associated with response to chronic hepatitis C interferon-alpha and ribavirin therapy. Nat Genet 2009;41:1100–4. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
