Anxiolytic Effects of Music Interventions in Patients Receiving Incenter Hemodialysis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 26462307
- PMCID: PMC10188276
Anxiolytic Effects of Music Interventions in Patients Receiving Incenter Hemodialysis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
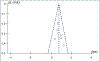
Music interventions are effectively used to reduce anxiety in patients on maintenance hemodialysis (HD). The purpose of this review was to identify the methodological quality and examine the effectiveness of music interventions on anxiety in patients requiring maintenance HD. Articles were searched through 10 electronic databases, and relevant articles were systematically reviewed. Seven studies were analyzed for this study, and the combined seven studies revealed a medium effect size (pooled standardized mean differences [SMD] = 0.76; 95% CI: 0.55, 0.98). This study found that music interventions effectively reduce anxiety in patients on maintenance HD.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- American Psychiatric Association (APA). (2013). The diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. (DSM-5) (5th ed.). Washington, DC: Author.
-
- Bae YS (2009). The effects of music therapy in fatigue and anxiety in hemodialysis patients. Master’s thesis, Dong-Eui University, Busan, Korea.
-
- Beathard GA, Urbanes A, Litchfield T, & Weinstein A (2011). The risk of sedation analgesia in hemodialysis patients undergoing interventional procedures. Seminars in Dialysis, 24(1), 97–103. - PubMed
-
- Birmelé B, Le Gall A, Sautenet B, Aguerre C, & Camus V (2012). Clinical, sociodemographic, and psychological correlates of health-related quality of life in chronic hemodialysis patients. Psychosomatics, 53(1), 30–37. - PubMed
-
- Borenstein M, Hedges LV, Higgins JPT, & Rothstein HR (2009) Introduction to meta-analysis. West Sussex, UK: Wiley.
