[The gene mutation analysis of a Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome family with normal mean platelet volume]
- PMID: 26462775
- PMCID: PMC7342700
- DOI: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-2727.2015.09.007
[The gene mutation analysis of a Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome family with normal mean platelet volume]
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the history of a Wiskott- Aldrich syndrome (WAS) family with normal mean platelet volume (MPV), analyse the WASP gene mutation of to better understand its clinical characteristics.
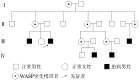
Methods: A four- generation WAS family histories of 22 members were investigated. Peripheral blood samples were collected from propositus and his mother to analyse all exon mutations of WASP gene using sanger sequencing.
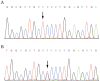
Results: The MPV of both propositus and his elder brother were normal. The patient's clinical score was 5, antibodies to PM-Scl, PCNA and PO were positive with very high level of ASO, the patient co- suffered from autoimmune disease, anemia, abnormal renal function, fungal infection and scleritis. A homozygous mutation (C>T) was found at 173 bp of exon 2, corresponding to amino acids Pro (P) 58 abnormally changed to Leu (L). His mother was the carrier of the mutation. Of 112 blood diseases- related genes, mutation frequencies of CBL, CREBBP, DNM2 and ADAMTS13 were higher than normals.
Conclusion: This was the first report the phenotype 173C>T mutation of WASP without eczema, but with normal MPV and autoimmune disease in Chinese, WAS should be recognized earlier and diagnosed correctly by genomic methods.
目的: 调查1个血小板平均体积(MPV)正常的Wiskott-Aldrich综合征(WAS)患者家系资料,分析先证者及其母亲WASP基因突变情况,探讨WAS的临床特征。
方法: 以1个四代共22人WAS家系为研究对象,调查该家系成员病史,采集先证者及母亲外周血标本并提取DNA,采用一代基因测序进行WASP基因全部外显子突变分析。
结果: 先证者及其哥哥MPV均正常。先证者WAS临床评分5分,抗PM-Scl抗体阳性,抗PCNA抗体阳性,抗核糖体P蛋白抗体阳性,抗链球菌溶血素明显增高。先证者合并有自身免疫性疾病、贫血、肾功能异常、真菌感染及巩膜炎。先证者WASP基因2号外显子173号碱基C>T纯合突变,导致第58号氨基酸由脯氨酸异变为亮氨酸。先证者母亲为WASP突变携带者。先证者CBL、CREBBP、DNM2及ADAMTS13基因突变频率明显高于正常人群。
结论: 该例WAS患者WASP基因173C>T突变,无湿疹,MPV正常,伴有自身免疫性疾病,为国内首次报道;其母亲为WASP突变携带者。WAS基因突变检测有助于早期识别和确诊WAS。
Figures
Similar articles
-
A novel WASP gene mutation in a Chinese boy with Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome.Int J Hematol. 2010 Sep;92(2):271-5. doi: 10.1007/s12185-010-0644-3. Epub 2010 Aug 4. Int J Hematol. 2010. PMID: 20683686
-
[Mutation analysis of WASP gene and prenatal diagnosis of Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2014 Sep;52(9):662-6. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25476427 Chinese.
-
Clinical and molecular characteristics of Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome in five unrelated Chinese families.Scand J Immunol. 2022 Jan;95(1):e13115. doi: 10.1111/sji.13115. Epub 2021 Nov 16. Scand J Immunol. 2022. PMID: 34758123
-
WASP-WIP complex in the molecular pathogenesis of Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome.Pediatr Int. 2016 Jan;58(1):4-7. doi: 10.1111/ped.12819. Epub 2015 Dec 5. Pediatr Int. 2016. PMID: 26331277 Review.
-
A Novel Mutation Leading to Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome in an Ethiopian Boy: a Case Report and a Review of Literature.J Clin Immunol. 2023 Aug;43(6):1272-1277. doi: 10.1007/s10875-023-01487-7. Epub 2023 Apr 13. J Clin Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37052865 Review.
Cited by
-
Case Report: Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome Caused by Extremely Skewed X-Chromosome Inactivation in a Chinese Girl.Front Pediatr. 2021 Jul 8;9:691524. doi: 10.3389/fped.2021.691524. eCollection 2021. Front Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34307257 Free PMC article.
-
A novel mutation in Wiskott-Aldrich gene manifesting as macrothrombocytopenia and neutropenia.BMJ Case Rep. 2018 Jul 10;2018:bcr2018225123. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2018-225123. BMJ Case Rep. 2018. PMID: 29991546 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Proust A, Guillet B, Pellier I, et al. Recurrent V75M mutation within the Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein: description of a homozygous female patient[J] Eur J Haematol. 2005;75(1):54–59. - PubMed
-
- Massaad MJ, Ramesh N, Geha RS. Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome: a comprehensive review[J] Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2013;1285:26–43. - PubMed
-
- Ariga T. Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome; an x-linked primary immunodeficiency disease with unique and characteristic features[J] Allergol Int. 2012;61(2):183–189. - PubMed
-
- Gulácsy V, Maródi L. Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome[J] Orv Hetil. 2008;149(29):1367–1371. - PubMed
-
- Zhu Q, Watanabe C, Liu T, et al. Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome/X-linked thrombocytopenia: WASP gene mutations, protein expression, and phenotype[J] Blood. 1997;90(7):2680–2689. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous