An automated real-time integration and interoperability framework for bioinformatics
- PMID: 26464306
- PMCID: PMC4603302
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-015-0761-3
An automated real-time integration and interoperability framework for bioinformatics
Abstract
Background: In recent years data integration has become an everyday undertaking for life sciences researchers. Aggregating and processing data from disparate sources, whether through specific developed software or via manual processes, is a common task for scientists. However, the scope and usability of the majority of current integration tools fail to deal with the fast growing and highly dynamic nature of biomedical data.
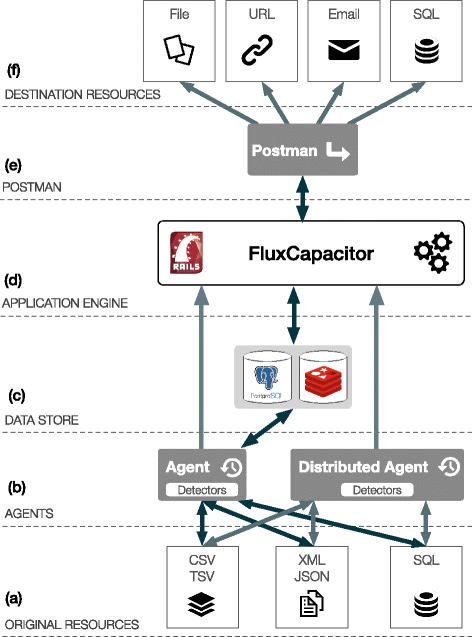
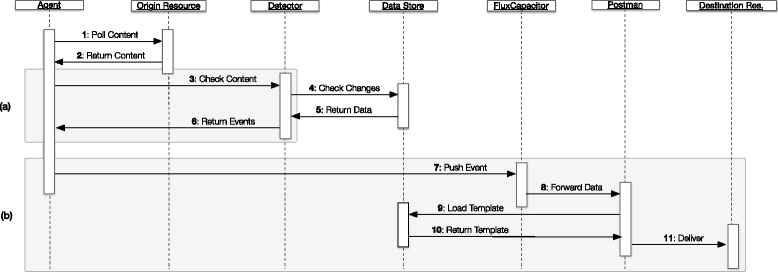
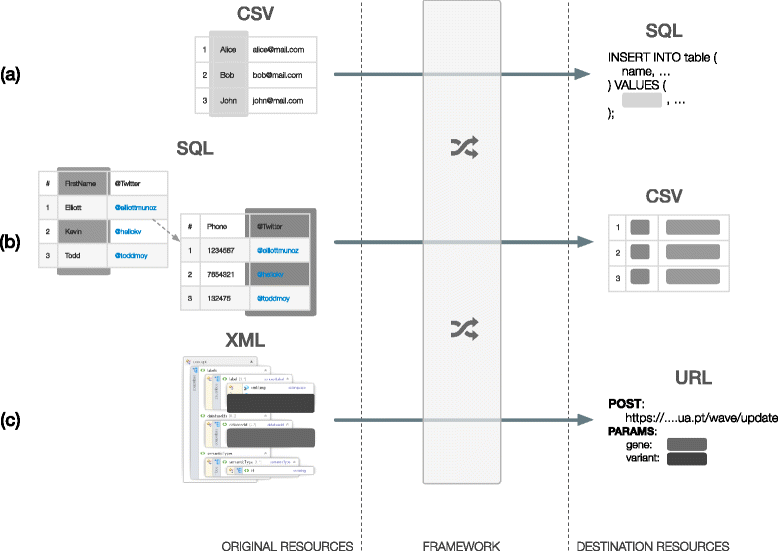
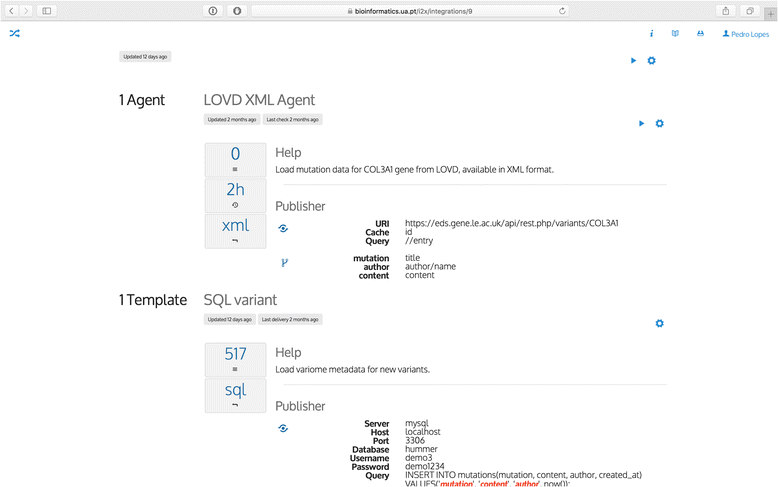
Results: In this work we introduce a reactive and event-driven framework that simplifies real-time data integration and interoperability. This platform facilitates otherwise difficult tasks, such as connecting heterogeneous services, indexing, linking and transferring data from distinct resources, or subscribing to notifications regarding the timeliness of dynamic data. For developers, the framework automates the deployment of integrative and interoperable bioinformatics applications, using atomic data storage for content change detection, and enabling agent-based intelligent extract, transform and load tasks.
Conclusions: This work bridges the gap between the growing number of services, accessing specific data sources or algorithms, and the growing number of users, performing simple integration tasks on a recurring basis, through a streamlined workspace available to researchers and developers alike.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Biowep: a workflow enactment portal for bioinformatics applications.BMC Bioinformatics. 2007 Mar 8;8 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S19. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-8-S1-S19. BMC Bioinformatics. 2007. PMID: 17430563 Free PMC article.
-
Serverless computing in omics data analysis and integration.Brief Bioinform. 2022 Jan 17;23(1):bbab349. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbab349. Brief Bioinform. 2022. PMID: 34505137 Free PMC article.
-
Intelligent client for integrating bioinformatics services.Bioinformatics. 2006 Jan 1;22(1):106-11. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti740. Epub 2005 Oct 27. Bioinformatics. 2006. PMID: 16257987
-
Automation of in-silico data analysis processes through workflow management systems.Brief Bioinform. 2008 Jan;9(1):57-68. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbm056. Epub 2007 Dec 2. Brief Bioinform. 2008. PMID: 18056132 Review.
-
Interoperability with Moby 1.0--it's better than sharing your toothbrush!Brief Bioinform. 2008 May;9(3):220-31. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbn003. Epub 2008 Jan 31. Brief Bioinform. 2008. PMID: 18238804 Review.
Cited by
-
TASKA: A modular task management system to support health research studies.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2019 Jul 2;19(1):121. doi: 10.1186/s12911-019-0844-6. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2019. PMID: 31266480 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thiam Yui C, Liang L, Jik Soon W, Husain W. A Survey on Data Integration in Bioinformatics. In: Abd Manaf A, Sahibuddin S, Ahmad R, Mohd Daud S, El-Qawasmeh E, editors. Informatics Engineering and Information Science. 254. Heidelberg: Springer Berlin; 2011. pp. 16–28.
-
- Darmont J, Boussaid O, Ralaivao J-C, Aouiche K. An architecture framework for complex data warehouses. arXiv preprint 2007. http://arxiv.org/abs/0707.1534.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

