Gene expression of IQGAPs and Ras families in an experimental mouse model for hepatocellular carcinoma: a mechanistic study of cancer progression
- PMID: 26464624
- PMCID: PMC4583856
Gene expression of IQGAPs and Ras families in an experimental mouse model for hepatocellular carcinoma: a mechanistic study of cancer progression
Abstract
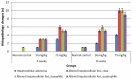
IQGAPs genes play critical role in either induction or suppression of cancer and its progression, however the relationship between Ras genes and these genes are still unclear. In this study, we tried to understand the mechanistic action of IQGAPs genes and its correlation with Ras genes in mouse hepatic cancer model. The genetic expressions of IQGAP1, IQGAP2, IQGAP3, Hras, Kras, Nras, Mras, Caspase3, and BAX were followed in both hepatocellular carcinoma and normal liver cells of Balbc mice. Genotoxic agent diethylnitrosamine (DEN)-induced hepatic cancer model was induced in male mice and recorded the occurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma by morphological and histological changes in the liver. It was observed that mRNA expressions of IQGAP1, Hras, Kras, Nras, Mras, Caspase3, and BAX genes were highly elevated in hepatocellular carcinoma cells when compared with normal liver cells, additionally their expressions increased by concentrating the dose of DEN. While, the expressions of IQGAP2 and IQGAP3 were significantly decreased in hepatocellular carcinoma cells when compared with normal liver cells, as well as their expressions decreased more with increasing the dose of DEN. It was concluded from this study that IQGAP1 has a strong signaling relationship with Ras genes in induction of cancer and it is considered as a key gene for induction or suppression of the hepatocellular carcinoma.
Keywords: DEN; IQGAP1; IQGAPs; hepatocellular carcinoma; ras.
Figures






References
-
- Schmidt VA, Scudder L, Devoe CE, Bernards A, Cupit LD, Bahou WF. IQGAP2 functions as a GTP-dependent effector protein in thrombin-induced platelet cytoskeletal reorganization. Blood. 2003;101:3021–3028. - PubMed
-
- Moradpour D, Wands JR. The molecular pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Viral Hepat. 1994;1:17–31. - PubMed
-
- Karami A, Alavian S, Najafi A, Hosseini MJ. Molecular Aspects of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Caused by Hepatitis C Virus. Hepatitis Monthly. 2006;6:75–82.
-
- Binato M, Kruel Schmidt M, Silveira Volkweis B, Behrend G, Isabel EM, Ricachenevsky GR. Mouse model of diethylnitrosamine-induced gastric cancer. J Surg Res. 2008;148:152–157. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
