Diode Laser in Minor Oral Surgery: A Case Series of Laser Removal of Different Benign Exophytic Lesions
- PMID: 26464782
- PMCID: PMC4599201
- DOI: 10.15171/jlms.2015.08
Diode Laser in Minor Oral Surgery: A Case Series of Laser Removal of Different Benign Exophytic Lesions
Abstract
Introduction: The role of laser in conservative management of oral disease is well established. Laser procedures are common in the fields of oral surgery, implant dentistry, endodontic, and periodontic therapy.
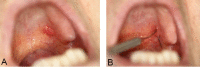
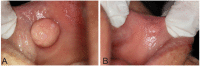
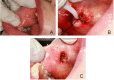
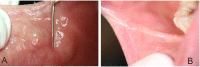
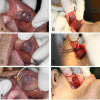
Case: This case series describes the use of diode laser for the excision of oral exophytic lesions. All the patients attended the oral medicine department of Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran. Criteria in patient selection were accessibility to lesions, patient fear from blade surgery, aesthetics, and probability of bleeding. An informed consent was filled by every patient. All of the lesions were completely excised under local anaesthesia by diode laser with 300 μm-fibre tip, 808 nm continuous wavelength and 3-3.5 W power for 3×60 seconds (Dr Smile, Italia). During surgery, the fibre tip was in contact with lesions. No analgesics were prescribed to the patients. The patients were followed for the first, second, and forth week after treatment.
Conclusion: The lesions could be excised using the diode laser. This procedure was a quick clinical technique without bleeding.
Keywords: Benign exophytic lesions; Diode laser; Oral.
Figures
References
-
- Eliades A, Stavrianos C, Kokkas A, Kafas P, Nazaroglou I. 808 nm diode laser in oral surgery: a case report of laser removal of fibroma. Res J Med Sci. 2010;4(3):175–8. doi: 10.3923/rjmsci.2010.175.178. - DOI
-
- Pai JB, Padma R, Divya Malagi S, Kamath V, Shridhar A, Mathews A. Excision of fibroma with diode laser: a case series. J Dent Lasers. 2014;8(1):34–38. doi: 10.4103/0976-2868.134124. - DOI
-
- Kalyanyama BM, Matee MI, Vuhahula E. Oral tumours in Tanzanian children based on biopsy materials examined over 15-year period from 1982 to 1997. Int Dent J. 2002;52:10–14. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources