p21(WAF1/CIP1) Expression is Differentially Regulated by Metformin and Rapamycin
- PMID: 26464852
- PMCID: PMC4590942
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/327640
p21(WAF1/CIP1) Expression is Differentially Regulated by Metformin and Rapamycin
Abstract
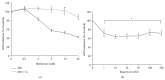
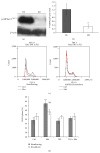
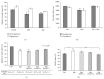
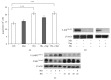
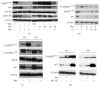
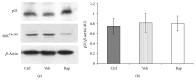
The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway plays an important role in the development of diabetic nephropathy and other age-related diseases. One of the features of DN is the elevated expression of p21(WAF1/CIP1). However, the importance of the mTOR signalling pathway in p21 regulation is poorly understood. Here we investigated the effect of metformin and rapamycin on mTOR-related phenotypes in cell lines of epithelial origin. This study reports that metformin inhibits high glucose-induced p21 expression. High glucose opposed metformin in regulating cell size, proliferation, and protein synthesis. These effects were associated with reduced AMPK activation, affecting downstream mTOR signalling. However, the inhibition of the mTOR pathway by rapamycin did not have a negative effect on p21 expression, suggesting that metformin regulates p21 upstream of mTOR. These findings provide support for the hypothesis that AMPK activation may regulate p21 expression, which may have implications for diabetic nephropathy and other age-related pathologies.
Figures



References
-
- Arya A., Aggarwal S., Yadav H. N. Pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2010;2(4):24–29.
-
- Wolf G. Molecular mechanisms of diabetic mesangial cell hypertrophy: a proliferation of novel factors. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology. 2002;13(10):2611–2613. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

