Oesophageal intrasquamous IgG4 deposits: an adjunctive marker to distinguish eosinophilic oesophagitis from reflux oesophagitis
- PMID: 26466342
- PMCID: PMC5717757
- DOI: 10.1111/his.12892
Oesophageal intrasquamous IgG4 deposits: an adjunctive marker to distinguish eosinophilic oesophagitis from reflux oesophagitis
Abstract
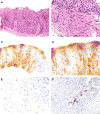
Aims: To explore the utility of an IgG4 immunohistochemical stain to help distinguish eosinophilic oesophagitis from gastroesophageal reflux disease.
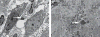
Methods and results: We examined 21 cases of eosinophilic oesophagitis and 25 cases of gastroesophageal reflux disease. The diagnosis of eosinophilic oesophagitis was based on the presence of oesophageal dysfunction, >15 eosinophils per high-power field, and a lack of response to proton pump inhibitors. Gastroesophageal reflux disease showed intraepithelial eosinophils, but a clinical and/or histological response to proton pump inhibitor therapy. We also evaluated an additional cohort of 22 cases with intraepithelial eosinophils. Immunohistochemical staining for IgG4 was performed. Sixteen of 21 (76%) eosinophilic oesophagitis cases showed intrasquamous extracellular IgG4 deposits, whereas all 25 gastroesophageal reflux disease cases were negative. Mucosal IgG4-positive plasma cells were identified in eosinophilic oesophagitis and gastroesophageal reflux disease cases in 58% and 40% of cases, respectively. Eosinophilic oesophagitis patients receiving treatment were less likely to be positive for intraepithelial IgG4 deposits (88% versus 53%). In the validation cohort, the sensitivity and specificity for eosinophilic oesophagitis were 88% and 100%, respectively.
Conclusions: The presence of intrasquamous IgG4 deposits is a useful adjunctive marker in the distinction between eosinophilic oesophagitis and gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Keywords: IgG4; IgG4-related disease; eosinophilic oesophagitis; reflux oesophagitis; ultrastructural evaluation.
© 2015 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Dellon ES, Gonsalves N, Hirano I, et al. ACG clinical guideline: evidenced based approach to the diagnosis and management of esophageal eosinophilia and eosinophilic esophagitis (EOE) Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2013;108:679–692. quiz 693. - PubMed
-
- Liacouras CA, Furuta GT, Hirano I, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis: updated consensus recommendations for children and adults. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011;128:3–20. quiz 21-–2. - PubMed
-
- Furuta GT, Liacouras CA, Collins MH, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis in children and adults: a systematic review and consensus recommendations for diagnosis and treatment. Gastroenterology. 2007;133:1342–1363. - PubMed
-
- Parfitt JR, Gregor JC, Suskin NG, Jawa HA, Driman DK. Eosinophilic esophagitis in adults: distinguishing features from gastroesophageal reflux disease: a study of 41 patients. Mod. Pathol. 2006;19:90–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

