Azathioprine-induced Acute Pancreatitis in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases--A Prospective Study on Incidence and Severity
- PMID: 26468141
- PMCID: PMC4692264
- DOI: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjv188
Azathioprine-induced Acute Pancreatitis in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases--A Prospective Study on Incidence and Severity
Abstract
Background and aims: Azathioprine [AZA] is recommended for maintenance of steroid-free remission in inflammatory bowel disease IBD. The aim of this study has been to establish the incidence and severity of AZA-induced pancreatitis, an idiosyncratic and major side effect, and to identify specific risk factors.
Methods: We studied 510 IBD patients [338 Crohn's disease, 157 ulcerative colitis, 15 indeterminate colitis] with initiation of AZA treatment in a prospective multicentre registry study. Acute pancreatitis was diagnosed in accordance with international guidelines.
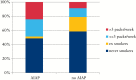
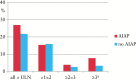
Results: AZA was continued by 324 [63.5%] and stopped by 186 [36.5%] patients. The most common cause of discontinuation was nausea [12.2%]. AZA-induced pancreatitis occurred in 37 patients [7.3%]. Of these: 43% were hospitalised with a median inpatient time period of 5 days; 10% had peripancreatic fluid collections; 24% had vomiting; and 14% had fever. No patient had to undergo nonsurgical or surgical interventions. Smoking was the strongest risk factor for AZA-induced acute pancreatitis [p < 0.0002] in univariate and multivariate analyses.
Conclusions: AZA-induced acute pancreatitis is a common adverse event in IBD patients, but in this study had a mild course in all patients. Smoking is the most important risk factor.
Keywords: Azathioprine; Crohn’s disease; inflammatory bowel disease; lipase; pancreatitis; smoking; ulcerative colitis.
© European Crohn’s and Colitis Organistion (ECCO) 2015.
Figures

References
-
- Travis SP, Stange EF, Lémann M, et al. ; European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation [ECCO]. European Evidence-based Consensus on the management of ulcerative colitis: Current management. J Crohns Colitis 2008;2:24–62. - PubMed
-
- Dignass A, Van Assche G, Lindsay JO, et al. ; European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation [ECCO]. The Second European Evidence-based Consensus on the diagnosis and management of Crohn’s disease: Current management. J Crohns Colitis 2010;4:28–62. - PubMed
-
- Qasim A, McDonald S, Sebastian S, et al. Efficacy and safety of 6-thioguanine in the management of inflammatory bowel disease. Scand J Gastroenterol 2007;42:194–9. - PubMed
-
- Bowen GE, Irons GV, Jr, Rhodes JB, Kirsner JB. Early experiences with azathioprine in ulcerative colitis; a note of caution. JAMA 1966;195:460–4. - PubMed
-
- Brooke BN, Hoffmann DC, Swarbrick ET. Azathioprine for Crohn’s disease. Lancet 1969;2:612–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

