The hematopoietic stem cell niche in homeostasis and disease
- PMID: 26468230
- PMCID: PMC4661168
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2015-07-533588
The hematopoietic stem cell niche in homeostasis and disease
Abstract
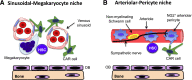
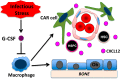
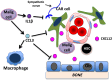
The bone marrow microenvironment contains a heterogeneous population of stromal cells organized into niches that support hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) and other lineage-committed hematopoietic progenitors. The stem cell niche generates signals that regulate HSC self-renewal, quiescence, and differentiation. Here, we review recent studies that highlight the heterogeneity of the stromal cells that comprise stem cell niches and the complexity of the signals that they generate. We highlight emerging data that stem cell niches in the bone marrow are not static but instead are responsive to environmental stimuli. Finally, we review recent data showing that hematopoietic niches are altered in certain hematopoietic malignancies, and we discuss how these alterations might contribute to disease pathogenesis.
© 2015 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures
References
-
- Enver T, Pera M, Peterson C, Andrews PW. Stem cell states, fates, and the rules of attraction. Cell Stem Cell. 2009;4(5):387–397. - PubMed
-
- Schofield R. The relationship between the spleen colony-forming cell and the haemopoietic stem cell. Blood Cells. 1978;4(1-2):7–25. - PubMed
-
- Kiger AA, Jones DL, Schulz C, Rogers MB, Fuller MT. Stem cell self-renewal specified by JAK-STAT activation in response to a support cell cue. Science. 2001;294(5551):2542–2545. - PubMed
-
- Kiger AA, White-Cooper H, Fuller MT. Somatic support cells restrict germline stem cell self-renewal and promote differentiation. Nature. 2000;407(6805):750–754. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

