The Inflammasome Adaptor ASC Induces Procaspase-8 Death Effector Domain Filaments
- PMID: 26468282
- PMCID: PMC4705927
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.687731
The Inflammasome Adaptor ASC Induces Procaspase-8 Death Effector Domain Filaments
Abstract
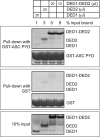
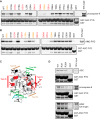
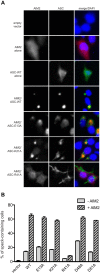
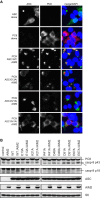
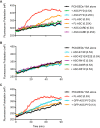
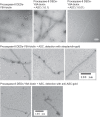
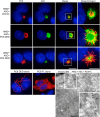
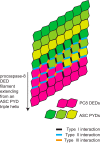
Inflammasomes mediate inflammatory and cell death responses to pathogens and cellular stress signals via activation of procaspases-1 and -8. During inflammasome assembly, activated receptors of the NLR or PYHIN family recruit the adaptor protein ASC and initiate polymerization of its pyrin domain (PYD) into filaments. We show that ASC filaments in turn nucleate procaspase-8 death effector domain (DED) filaments in vitro and in vivo. Interaction between ASC PYD and procaspase-8 tandem DEDs optimally required both DEDs and represents an unusual heterotypic interaction between domains of the death fold superfamily. Analysis of ASC PYD mutants showed that interaction surfaces that mediate procaspase-8 interaction overlap with those required for ASC self-association and interaction with the PYDs of inflammasome initiators. Our data indicate that multiple types of death fold domain filaments form at inflammasomes and that PYD/DED and homotypic PYD interaction modes are similar. Interestingly, we observed condensation of procaspase-8 filaments containing the catalytic domain, suggesting that procaspase-8 interactions within and/or between filaments may be involved in caspase-8 activation. Procaspase-8 filaments may also be relevant to apoptosis induced by death receptors.
Keywords: apoptosis; caspase; cell death; death domain; death domain filaments; inflammasome; pattern recognition receptor (PRR).
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Lamkanfi M., and Dixit V. M. (2014) Mechanisms and functions of inflammasomes. Cell 157, 1013–1022 - PubMed
-
- Li P., Allen H., Banerjee S., Franklin S., Herzog L., Johnston C., McDowell J., Paskind M., Rodman L., and Salfeld J. (1995) Mice deficient in IL-1 β-converting enzyme are defective in production of mature IL-1 β and resistant to endotoxic shock. Cell 80, 401–411 - PubMed
-
- Gu Y., Kuida K., Tsutsui H., Ku G., Hsiao K., Fleming M. A., Hayashi N., Higashino K., Okamura H., Nakanishi K., Kurimoto M., Tanimoto T., Flavell R. A., Sato V., Harding M. W., Livingston D. J., and Su M. S. (1997) Activation of interferon-γ inducing factor mediated by interleukin-1β converting enzyme. Science 275, 206–209 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

