Blood-Derived CD4 T Cells Naturally Resist Pyroptosis during Abortive HIV-1 Infection
- PMID: 26468749
- PMCID: PMC4627664
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2015.09.010
Blood-Derived CD4 T Cells Naturally Resist Pyroptosis during Abortive HIV-1 Infection
Abstract
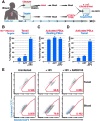
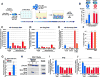
Progression to AIDS is driven by CD4 T cell depletion, mostly involving pyroptosis elicited by abortive HIV infection of CD4 T cells in lymphoid tissues. Inefficient reverse transcription in these cells leads to cytoplasmic accumulation of viral DNAs that are detected by the DNA sensor IFI16, resulting in inflammasome assembly, caspase-1 activation, and pyroptosis. Unexpectedly, we found that peripheral blood-derived CD4 T cells naturally resist pyroptosis. This resistance is partly due to their deeper resting state, resulting in fewer HIV-1 reverse transcripts and lower IFI16 expression. However, when co-cultured with lymphoid-derived cells, blood-derived CD4 T cells become sensitized to pyroptosis, likely recapitulating interactions occurring within lymphoid tissues. Sensitization correlates with higher levels of activated NF-κB, IFI16 expression, and reverse transcription. Blood-derived lymphocytes purified from co-cultures lose sensitivity to pyroptosis. These differences highlight how the lymphoid tissue microenvironment encountered by trafficking CD4 T lymphocytes dynamically shapes their biological response to HIV.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Cavrois M, De Noronha C, Greene W. A sensitive and specific enzyme-based assay detecting HIV-1 virion fusion in primary T lymphocytes. Nat Biotechnol. 2002;20:1151–1154. - PubMed
-
- Chen LF, Greene WC. Shaping the nuclear action of NF-kappaB. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2004;5:392–401. - PubMed
-
- Cyster JG. Chemokines, sphingosine-1-phosphate, and cell migration in secondary lymphoid organs. Annu Rev Immunol. 2005;23:127–159. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 AI007620/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- 1DP1036502/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- T32 AI060537/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR028962/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027763/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI102782/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR028962-01/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI096113/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AL007620-04/PHS HHS/United States
- R21AI102782/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19AI0961133/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DP1 DA036502/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

