Biomarker for Spinal Muscular Atrophy: Expression of SMN in Peripheral Blood of SMA Patients and Healthy Controls
- PMID: 26468953
- PMCID: PMC4607439
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0139950
Biomarker for Spinal Muscular Atrophy: Expression of SMN in Peripheral Blood of SMA Patients and Healthy Controls
Abstract
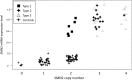
Spinal muscular atrophy is caused by a functional deletion of SMN1 on Chromosome 5, which leads to a progressive loss of motor function in affected patients. SMA patients have at least one copy of a similar gene, SMN2, which produces functional SMN protein, although in reduced quantities. The severity of SMA is variable, partially due to differences in SMN2 copy numbers. Here, we report the results of a biomarker study characterizing SMA patients of varying disease severity. SMN copy number, mRNA and Protein levels in whole blood of patients were measured and compared against a cohort of healthy controls. The results show differential regulation of expression of SMN2 in peripheral blood between patients and healthy subjects.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Brzustowicz LM, Lehner T, Castilla LH, Penchaszadeh GK, Wilhelmsen KC, Daniels R, et al. (1990) Genetic mapping of chronic childhood-onset spinal muscular atrophy to chromosome 5q11.2–13.3. Nature 344: 540–541. - PubMed
-
- Lefebvre S, Burglen L, Reboullet S, Clermont O, Burlet P, Viollet L, et al. (1995) Identification and characterization of a spinal muscular atrophy-determining gene. Cell 80: 155–165. - PubMed
-
- Monani UR, Lorson CL, Parsons DW, Prior TW, Androphy EJ, Burghes AH, et al. (1999) A single nucleotide difference that alters splicing patterns distinguishes the SMA gene SMN1 from the copy gene SMN2. Hum Mol Genet 8: 1177–1183. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

