Implicit Racial/Ethnic Bias Among Health Care Professionals and Its Influence on Health Care Outcomes: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 26469668
- PMCID: PMC4638275
- DOI: 10.2105/AJPH.2015.302903
Implicit Racial/Ethnic Bias Among Health Care Professionals and Its Influence on Health Care Outcomes: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Background: In the United States, people of color face disparities in access to health care, the quality of care received, and health outcomes. The attitudes and behaviors of health care providers have been identified as one of many factors that contribute to health disparities. Implicit attitudes are thoughts and feelings that often exist outside of conscious awareness, and thus are difficult to consciously acknowledge and control. These attitudes are often automatically activated and can influence human behavior without conscious volition.
Objectives: We investigated the extent to which implicit racial/ethnic bias exists among health care professionals and examined the relationships between health care professionals' implicit attitudes about racial/ethnic groups and health care outcomes.
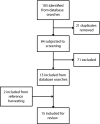
Search methods: To identify relevant studies, we searched 10 computerized bibliographic databases and used a reference harvesting technique.
Selection criteria: We assessed eligibility using double independent screening based on a priori inclusion criteria. We included studies if they sampled existing health care providers or those in training to become health care providers, measured and reported results on implicit racial/ethnic bias, and were written in English.
Data collection and analysis: We included a total of 15 studies for review and then subjected them to double independent data extraction. Information extracted included the citation, purpose of the study, use of theory, study design, study site and location, sampling strategy, response rate, sample size and characteristics, measurement of relevant variables, analyses performed, and results and findings. We summarized study design characteristics, and categorized and then synthesized substantive findings.
Main results: Almost all studies used cross-sectional designs, convenience sampling, US participants, and the Implicit Association Test to assess implicit bias. Low to moderate levels of implicit racial/ethnic bias were found among health care professionals in all but 1 study. These implicit bias scores are similar to those in the general population. Levels of implicit bias against Black, Hispanic/Latino/Latina, and dark-skinned people were relatively similar across these groups. Although some associations between implicit bias and health care outcomes were nonsignificant, results also showed that implicit bias was significantly related to patient-provider interactions, treatment decisions, treatment adherence, and patient health outcomes. Implicit attitudes were more often significantly related to patient-provider interactions and health outcomes than treatment processes.
Conclusions: Most health care providers appear to have implicit bias in terms of positive attitudes toward Whites and negative attitudes toward people of color. Future studies need to employ more rigorous methods to examine the relationships between implicit bias and health care outcomes. Interventions targeting implicit attitudes among health care professionals are needed because implicit bias may contribute to health disparities for people of color.
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. CDC health disparities and inequalities report—United States, 2013. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2013;62(suppl 3):1–187. - PubMed
-
- Fiscella K, Franks P, Gold MR, Clancy CM. Inequality in quality: addressing socioeconomic, racial, and ethnic disparities in health care. JAMA. 2000;283(19):2579–2584. - PubMed
-
- Mayberry RM, Mili F, Ofili E. Racial and ethnic differences in access to medical care. Med Care Res Rev. 2000;57(suppl 1):108–145. - PubMed
-
- 2013 National Healthcare Disparities Report. Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, US Dept of Health and Human Services; 2014.
-
- Beckman HB, Frankel RM. The effect of physician behavior on the collection of data. Ann Intern Med. 1984;101(5):692–696. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical