Lectin staining and flow cytometry reveals female-induced sperm acrosome reaction and surface carbohydrate reorganization
- PMID: 26470849
- PMCID: PMC4607886
- DOI: 10.1038/srep15321
Lectin staining and flow cytometry reveals female-induced sperm acrosome reaction and surface carbohydrate reorganization
Abstract
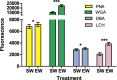
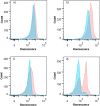
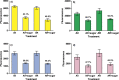
All cells are covered by glycans, an individually unique layer of oligo- and polysaccharides that are critical moderators of self-recognition and other cellular-level interactions (e.g. fertilization). The functional similarity between these processes suggests that gamete surface glycans may also have an important, but currently overlooked, role in sexual selection. Here we develop a user-friendly methodological approach designed to facilitate future tests of this possibility. Our proposed method is based on flow cytometric quantification of female-induced sperm acrosome reaction and sperm surface glycan modifications in the Mediterranean mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis. In this species, as with many other taxa, eggs release water-soluble factors that attract conspecific sperm (chemoattraction) and promote potentially measurable changes in sperm behavior and physiology. We demonstrate that flow cytometry is able to identify sperm from other seawater particles as well as accurately measure both acrosome reaction and structural modifications in sperm glycans. This methodological approach can increase our understanding of chemically-moderated gamete-level interactions and individual-specific gamete recognition in Mytilus sp. and other taxa with similar, easily identifiable acrosome structure. Our approach is also likely to be applicable to several other species, since carbohydrate-mediated cellular-level interactions between gametes are universal among externally and internally fertilizing species.
Figures



References
-
- Swanson W. J. & Vacquier V. D. The rapid evolution of reproductive proteins. Nat. Rev. Genet. 3, 137–144 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Miyata S. et al. Flagellasialin: a novel sulfated α2,9-linked polysialic acid glycoprotein of sea urchin sperm flagella. Glycobiology 16, 1229–1241 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Hiyoshi W. et al. Egg jelly of the newt, Cynops pyrrhogaster contains a factor essential for sperm binding to the vitelline envelope. J. Exp. Zool. 307A, 301–311 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Hirohashi N. et al. Egg and sperm recognition systems during fertilization. Develop. Growth Differ. 50, S221–S238 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Wassarman P. M. The sperm’s sweet tooth. Science 333, 1708–1709 (2011). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

