MiR-449a suppresses the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by multiple targets
- PMID: 26471185
- PMCID: PMC4608176
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-015-1738-3
MiR-449a suppresses the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by multiple targets
Abstract
Background: Increasing evidence indicates that Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) can be regulated by microRNAs (miRNAs). MiR-449a is a liver abundant miRNA. However, the role of miR-449a in the metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains largely unknown.
Methods: The expression levels of miR-449a were first examined in HCC cell lines and tumour tissues by real-time PCR. The in vitro and in vivo functional effect and underlying molecular mechanisms of miR-449a were examined further.
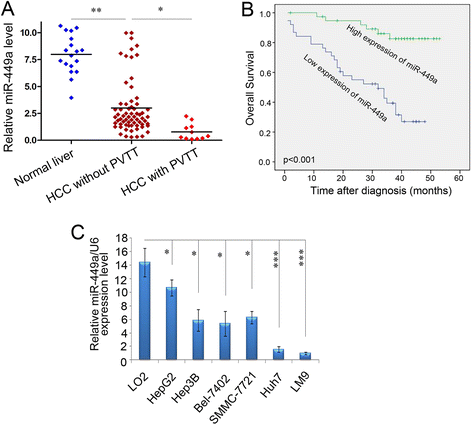
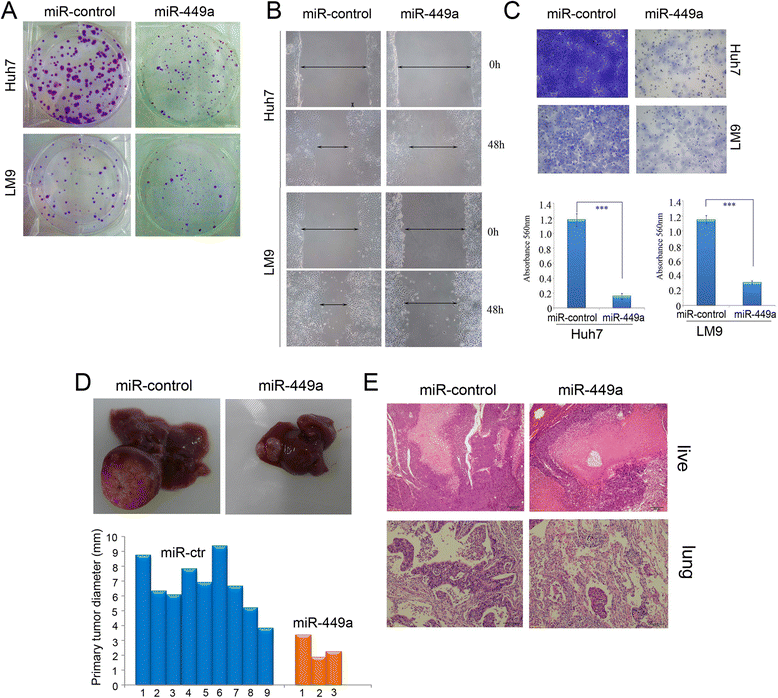
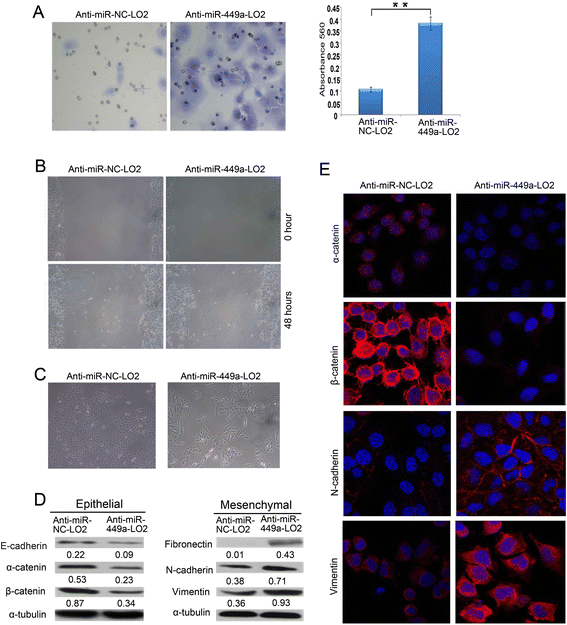
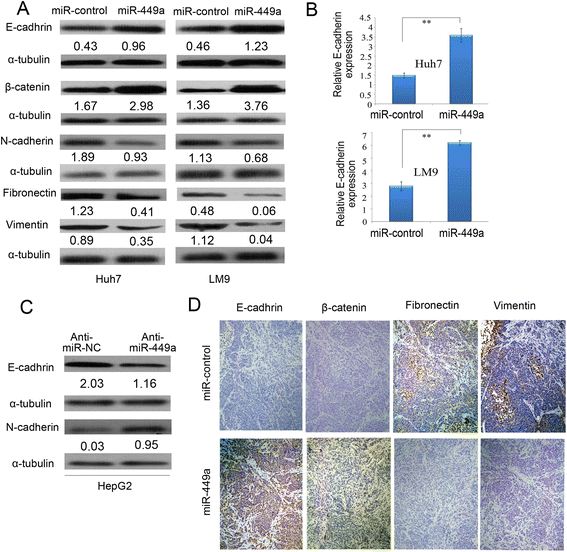
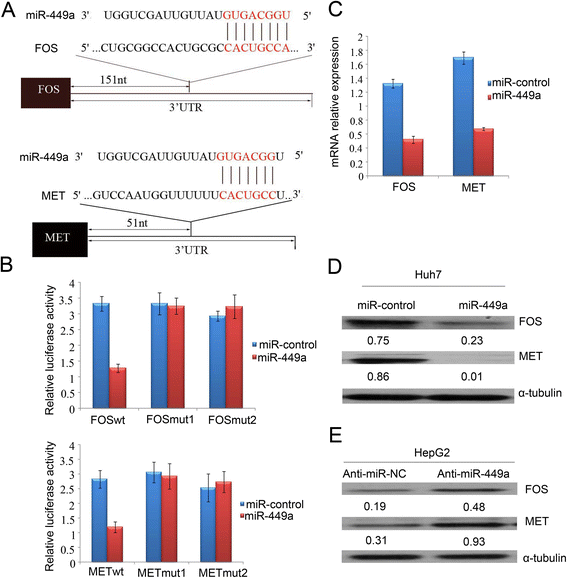
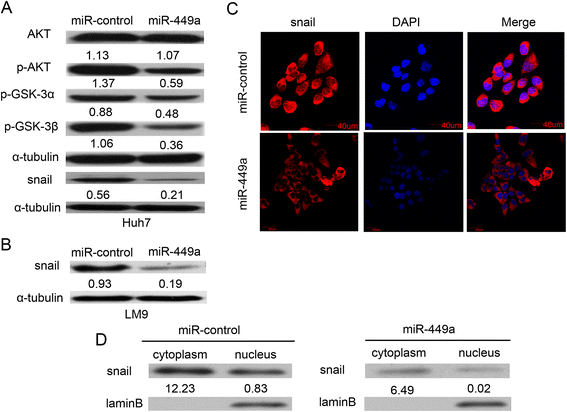
Results: In the present study, we found that miR-449a was significantly decreased in HCC cells and tissues, especially in those with the portal vein tumor thrombus. In HCC cell lines, stable overexpression of miR-449a was sufficient to inhibit cell motility in vitro, and pulmonary metastasis in vivo. In addition, ectopic overexpression of miR-449a in HCC cells promoted the expression of epithelial markers and reduced the levels of mesenchymal markers. Further studies revealed that the reintroduction of miR-449a attenuated the downstream signaling of Met, and consequently reduced the accumulation of Snail in cell nucleus by targeting the 3'-untranslated regions (3'-UTR) of FOS and Met.
Conclusions: Our data highlight an important role of miR-449a in the molecular etiology of HCC, and implicate the potential application of miR-449a in cancer therapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-148a suppresses the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of hepatoma cells by targeting Met/Snail signaling.Oncogene. 2014 Jul 31;33(31):4069-76. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.369. Epub 2013 Sep 9. Oncogene. 2014. PMID: 24013226
-
MicroRNA-451: epithelial-mesenchymal transition inhibitor and prognostic biomarker of hepatocelluar carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2015 Jul 30;6(21):18613-30. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4317. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26164082 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-122 inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting Snail1 and Snail2 and suppressing WNT/β-cadherin signaling pathway.Exp Cell Res. 2017 Nov 15;360(2):210-217. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2017.09.010. Epub 2017 Sep 8. Exp Cell Res. 2017. PMID: 28890291
-
MicroRNAs involved with hepatocellular carcinoma (Review).Oncol Rep. 2015 Dec;34(6):2811-20. doi: 10.3892/or.2015.4275. Epub 2015 Sep 15. Oncol Rep. 2015. PMID: 26398882 Review.
-
The Role of the MiR-181 Family in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cells. 2024 Jul 31;13(15):1289. doi: 10.3390/cells13151289. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39120319 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Integrative Network Analysis Reveals a MicroRNA-Based Signature for Prognosis Prediction of Epithelial Ovarian Cancer.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Jun 4;2019:1056431. doi: 10.1155/2019/1056431. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31275959 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNAs: Emerging Role in Cancer Diagnostics and Therapeutics.Front Mol Biosci. 2020 Oct 28;7:577938. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2020.577938. eCollection 2020. Front Mol Biosci. 2020. PMID: 33195421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional Repression and Protein Degradation of the Ca2+-Activated K+ Channel KCa1.1 by Androgen Receptor Inhibition in Human Breast Cancer Cells.Front Physiol. 2018 Apr 16;9:312. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00312. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29713287 Free PMC article.
-
Noncoding RNAs in breast cancer.Brief Funct Genomics. 2016 May;15(3):200-21. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/elv055. Epub 2015 Dec 18. Brief Funct Genomics. 2016. PMID: 26685283 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Loss of miR-449a in ERG-associated prostate cancer promotes the invasive phenotype by inducing SIRT1.Oncotarget. 2016 Apr 19;7(16):22791-806. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8061. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26988912 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Oishi N, Kumar MR, Roessler S, Ji J, Forgues M, Budhu A, et al. Transcriptomic profiling reveals hepatic stem-like gene signatures and interplay of miR-200c and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology. 2012;56(5):1792–1803. doi: 10.1002/hep.25890. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

