Spinal inhibition of p38 MAP kinase reduces inflammatory and neuropathic pain in male but not female mice: Sex-dependent microglial signaling in the spinal cord
- PMID: 26472019
- PMCID: PMC5502100
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbi.2015.10.006
Spinal inhibition of p38 MAP kinase reduces inflammatory and neuropathic pain in male but not female mice: Sex-dependent microglial signaling in the spinal cord
Abstract
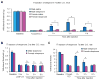
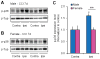
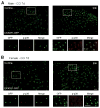
Previous studies have shown that activation of p38 mitogen-activating kinase (MAPK) in spinal microglia participates in the generation of inflammatory and neuropathic pain in various rodent models. However, these studies focused on male mice to avoid confounding effects of the estrous cycle of females. Recent studies have shown that some spinal pro-inflammatory signaling such as Toll-like receptor 4-mediated signaling contributes to pain hypersensitivity only in male mice. In this study we investigated the distinct role of spinal p38 in inflammatory and neuropathic pain using a highly selective p38 inhibitor skepinone. Intrathecal injection of skepinone prevented formalin induced inflammatory pain in male but not female mice. Furthermore, intrathecal skepinone reduced chronic constriction injury (CCI) induced neuropathic pain (mechanical allodynia) in male mice on CCI-day 7 but not CCI-day 21. This male-dependent inhibition of neuropathic pain also occurred in rats following intrathecal skepinone. Nerve injury induced spinal p38 activation (phosphorylation) in CX3CR1-GFP(+) microglia on CCI-day 7, and this activation was more prominent in male mice. In contrast, CCI induced comparable microgliosis and expression of the microglial markers CX3CR1 and IBA-1 in both sexes. Notably, intraperitoneal or local perineural administration of skepinone inhibited CCI-induced mechanical allodynia in both sexes of mice. Finally, skepinone only reduced the frequency of spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic currents (sEPSCs) in lamina IIo neurons of spinal cord slices of males 7days post CCI. Therefore, the sex-specific p38 activation and signaling is confined to the spinal cord in inflammatory and neuropathic pain conditions.
Keywords: Inflammatory pain; MAPK; Male; Microglia; Neuropathic pain; Sex; p38.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors have no competing financial interest in this study.
Figures





References
-
- Anand P, Shenoy R, Palmer JE, Baines AJ, Lai RY, Robertson J, Bird N, Ostenfeld T, Chizh BA. Clinical trial of the p38 MAP kinase inhibitor dilmapimod in neuropathic pain following nerve injury. Eur J Pain. 2011;15:1040–1048. - PubMed
-
- Bennett GJ, Xie YK. A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen in man. Pain. 1988;33:87–107. - PubMed
-
- Brown CM, Xu Q, Okhubo N, Vitek MP, Colton CA. Androgen-mediated immune function is altered by the apolipoprotein E gene. Endocrinology. 2007 Mar 31;:3383–3390. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

