Myocardial NF-κB activation is essential for zebrafish heart regeneration
- PMID: 26472034
- PMCID: PMC4629358
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1511209112
Myocardial NF-κB activation is essential for zebrafish heart regeneration
Abstract
Heart regeneration offers a novel therapeutic strategy for heart failure. Unlike mammals, lower vertebrates such as zebrafish mount a strong regenerative response following cardiac injury. Heart regeneration in zebrafish occurs by cardiomyocyte proliferation and reactivation of a cardiac developmental program, as evidenced by induction of gata4 regulatory sequences in regenerating cardiomyocytes. Although many of the cellular determinants of heart regeneration have been elucidated, how injury triggers a regenerative program through dedifferentiation and epicardial activation is a critical outstanding question. Here, we show that NF-κB signaling is induced in cardiomyocytes following injury. Myocardial inhibition of NF-κB activity blocks heart regeneration with pleiotropic effects, decreasing both cardiomyocyte proliferation and epicardial responses. Activation of gata4 regulatory sequences is also prevented by NF-κB signaling antagonism, suggesting an underlying defect in cardiomyocyte dedifferentiation. Our results implicate NF-κB signaling as a key node between cardiac injury and tissue regeneration.
Keywords: NF-κB; cardiomyocyte; epicardium; heart regeneration; zebrafish.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


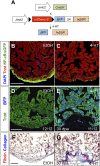



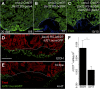
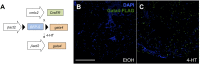

Similar articles
-
Nrg1 is an injury-induced cardiomyocyte mitogen for the endogenous heart regeneration program in zebrafish.Elife. 2015 Apr 1;4:e05871. doi: 10.7554/eLife.05871. Elife. 2015. PMID: 25830562 Free PMC article.
-
The regenerative capacity of the zebrafish heart is dependent on TGFβ signaling.Development. 2012 Jun;139(11):1921-30. doi: 10.1242/dev.078543. Epub 2012 Apr 18. Development. 2012. PMID: 22513374
-
A dual epimorphic and compensatory mode of heart regeneration in zebrafish.Dev Biol. 2015 Mar 1;399(1):27-40. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2014.12.002. Epub 2014 Dec 31. Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 25557620
-
Building and re-building the heart by cardiomyocyte proliferation.Development. 2016 Mar 1;143(5):729-40. doi: 10.1242/dev.132910. Development. 2016. PMID: 26932668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular and Molecular Mechanism of Cardiac Regeneration: A Comparison of Newts, Zebrafish, and Mammals.Biomolecules. 2020 Aug 19;10(9):1204. doi: 10.3390/biom10091204. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32825069 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A hyperactivating proinflammatory RIPK2 allele associated with early-onset osteoarthritis.Hum Mol Genet. 2018 Jul 1;27(13):2383-2391. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddy132. Hum Mol Genet. 2018. PMID: 29659823 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammation and matrix metalloproteinase 9 (Mmp-9) regulate photoreceptor regeneration in adult zebrafish.Glia. 2020 Jul;68(7):1445-1465. doi: 10.1002/glia.23792. Epub 2020 Feb 8. Glia. 2020. PMID: 32034934 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Netrin downstream of overactive Hedgehog signaling disrupts optic fissure formation.Dev Dyn. 2025 Feb;254(2):158-173. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.733. Epub 2024 Aug 21. Dev Dyn. 2025. PMID: 39166841 Free PMC article.
-
Directed Differentiation of Zebrafish Pluripotent Embryonic Cells to Functional Cardiomyocytes.Stem Cell Reports. 2016 Sep 13;7(3):370-382. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2016.07.020. Epub 2016 Aug 25. Stem Cell Reports. 2016. PMID: 27569061 Free PMC article.
-
Myocardial plasticity: cardiac development, regeneration and disease.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2016 Oct;40:120-130. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2016.05.029. Epub 2016 Aug 4. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2016. PMID: 27498024 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mozaffarian D, et al. American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee Heart disease and stroke statistics--2015 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2015;131(4):e29–e322. - PubMed
-
- Poss KD, Wilson LG, Keating MT. Heart regeneration in zebrafish. Science. 2002;298(5601):2188–2190. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

