Pediatric emergency room activities in Italy: a national survey
- PMID: 26472091
- PMCID: PMC4608128
- DOI: 10.1186/s13052-015-0184-9
Pediatric emergency room activities in Italy: a national survey
Abstract
Background: In Italy, the number of accesses to the Emergency Units has been growing for the past 30 years. This, together with a low coordination between hospital and peripheral pediatric services, has brought to an unnecessarily high number of hospital admissions. For this reason, it is essential to plan and implement strategies able to improve the appropriateness of hospital admissions. In the '90s, the Short Stay Observation was extended to pediatric patients. As highlighted by the report "Guidelines for Pediatric Observation Units" (2005), patients receive considerable benefits from a short hospital permanence. The purpose of the study is to report data about the Pediatric Emergency Room activities in Italy.
Methods: In 2011, the Italian Society of Pediatrics promoted an online data collection to investigate organization and activity of Italian Pediatric and Neonatal Units. A form, containing 140 questions, was sent to 624 Pediatric and Neonatology Units. This study will be focused only on data regarding pediatric Emergency Rooms (E.R.) and Observation Units.
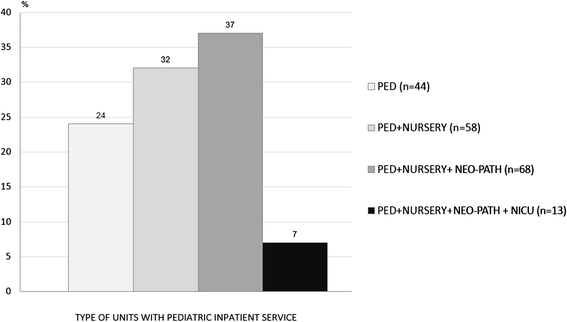
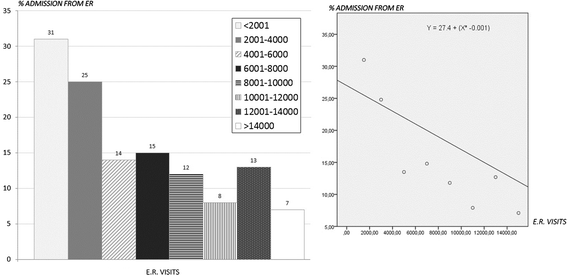
Results: 237 units replied, 183 if we focus on units with pediatric inpatient service. Based on the results, E.R Units were provided with a dedicated pediatrician in 56 % of the cases: of these, 85 % for 24 h. The majority of the patients were seen by a pediatrician. In only 8 % of the units, patients visited by a pediatrician were less than 40 %. The age limit was 14 years in 60 % of the cases. In 72 % of participating units a E.R. triage was carried out. Only 18 % of units registered more than 10000 E.R. visits/year. The percentage of children hospitalized after accessing the E.R. was significantly higher in southern regions (more than 20 % of the units hospitalized more than 40 % of children entering the E.R.). 66 % of the units were provided with an Observation Unit. In 61 % of the cases, the duration did not exceed 24 h. In more than half of the structures, less than 10 % of the E.R. visits went into observation. The type of remuneration was not homogeneous.
Conclusions: The study highlights the heterogeneity of the Italian reality, with great possibilities for improvement, especially in southern regions.
Figures


References
-
- Ministero della Salute Commissione Consultiva: Piano per il miglioramento del Sistema di Emergenza/Urgenza. Linee Guida per la riorganizzazione dei servizi di emergenza ed urgenza pediatrica. Accessed online http://www.salute.gov.it/imgs/C_17pubblicazioni_856_ulterioriallegati_ul... (2005).
-
- Consensus Meeting L’Osservazione Temporanea Breve in Pronto Soccorso Pediatrico: Linee Guida per la gestione dell’Osservazione Breve in Pediatria: 14-15 October 2005; Trieste. Accessed online http://www.sime2up.com/doc/1748718914_DocumentofinaleConsensusOT.pdf (2005).
-
- Longhi R. Indagine della Società Italiana di Pediatria sullo stato della rete pediatrica ospedaliera in Italia. Atti 65° congresso Nazionale S.I.P., Padova 2009. Minerva Pediatr. 2009;61:6–8.
-
- Materia E, Fortino A, Lispi L. La valutazione dell’appropriatezza dei ricoveri ospedalieri in Italia. Accessed online http://www.salute.gov.it/imgs/C_17_pubblicazioni_1001_allegato.pdf (2002).
-
- Perletti L, Parizzi F, Gargantini G, Lispi L, Alfò M. La razionalizzazione del ricovero ospedaliero in età pediarica. Ospedale e Territorio. Accessed online http://www.salute.gov.it/imgs/C_17_pubblicazioni_999_allegato.pdf (2000).
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

