Expression of the Drosophila homeobox gene, Distal-less, supports an ancestral role in neural development
- PMID: 26472170
- PMCID: PMC4715519
- DOI: 10.1002/dvdy.24359
Expression of the Drosophila homeobox gene, Distal-less, supports an ancestral role in neural development
Abstract
Background: Distal-less (Dll) encodes a homeodomain transcription factor expressed in developing appendages of organisms throughout metazoan phylogeny. Based on earlier observations in the limbless nematode Caenorhabditis elegans and the primitive chordate amphioxus, it was proposed that Dll had an ancestral function in nervous system development. Consistent with this hypothesis, Dll is necessary for the development of both peripheral and central components of the Drosophila olfactory system. Furthermore, vertebrate homologs of Dll, the Dlx genes, play critical roles in mammalian brain development.
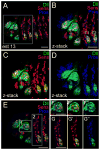
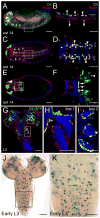
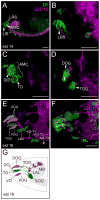
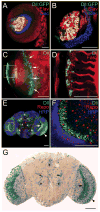
Results: Using fluorescent immunohistochemistry of fixed samples and multiphoton microscopy of living Drosophila embryos, we show that Dll is expressed in the embryonic, larval and adult central nervous system and peripheral nervous system (PNS) in embryonic and larval neurons, brain and ventral nerve cord glia, as well as in PNS structures associated with chemosensation. In adult flies, Dll expression is expressed in the optic lobes, central brain regions and the antennal lobes.
Conclusions: Characterization of Dll expression in the developing nervous system supports a role of Dll in neural development and function and establishes an important basis for determining the specific functional roles of Dll in Drosophila development and for comparative studies of Drosophila Dll functions with those of its vertebrate counterparts.
Keywords: Dll; Dlx; nervous system; olfaction; sensory system.
© 2015 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Alfonso T, Jones B. gcm2 promotes glial cell differentiation and is required with glial cells missing for macrophage development in Drosophila. Dev Biol. 2002;248:369–383. - PubMed
-
- Arendt D, Nubler-Jung K. Comparison of early nerve cord development in insects and vertebrates. Development. 1999;126:2309–2325. - PubMed
-
- Calleja M, Moreno E, Pelaz S, Morata G. Visualization of gene expression in living adult Drosophila. Science. 1996;274(5285):252–255. - PubMed
-
- Campbell G, Goring H, Lin T, Spana E, Andersson S, Doe CQ, Tomlinson A. RK2, a glial-specific homeodomain protein required for embryonic nerve cord condensation and viability in Drosophila. Development. 1994;120:2957–2966. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

