Genes, circuits, and precision therapies for autism and related neurodevelopmental disorders
- PMID: 26472761
- PMCID: PMC4739545
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aab3897
Genes, circuits, and precision therapies for autism and related neurodevelopmental disorders
Abstract
Research in the genetics of neurodevelopmental disorders such as autism suggests that several hundred genes are likely risk factors for these disorders. This heterogeneity presents a challenge and an opportunity at the same time. Although the exact identity of many of the genes remains to be discovered, genes identified to date encode proteins that play roles in certain conserved pathways: protein synthesis, transcriptional and epigenetic regulation, and synaptic signaling. The next generation of research in neurodevelopmental disorders must address the neural circuitry underlying the behavioral symptoms and comorbidities, the cell types playing critical roles in these circuits, and common intercellular signaling pathways that link diverse genes. Results from clinical trials have been mixed so far. Only when we can leverage the heterogeneity of neurodevelopmental disorders into precision medicine will the mechanism-based therapeutics for these disorders start to unlock success.
Copyright © 2015, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Figures
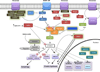


References
-
- Kanner L. Autistic disturbances of affective contact. Nervous Child. 1943;2:217–250. - PubMed
-
- Lord C. In: Understanding Autism: From Basic Neuroscience to Treatment. Moldin SO, Rubenstein JLR, editors. Boca Raton, FL: Taylor & Francis; 2006. pp. 1–23.
-
- Ganz M. In: Understanding Autism: From Basic Neuroscience to Treatment. Moldin SO, Rubenstein JLR, editors. Boca Raton, FL: Taylor & Francis; 2006. pp. 475–502.
-
- Gillberg C, Fernell E. Autism plus versus autism pure. J Autism Dev Disord. 2014;44:3274–3276. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- P20 NS080199/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- F32 EY007023/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EF1451125/PHS HHS/United States
- U54 NS092090/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 NS090473/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY007023/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY007023/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH085802/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- NS090473/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 HD018655/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 NS082320/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U54NS092090/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- MH085802/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

