Wound Healing Activity of a Traditionally Used Poly Herbal Product in a Burn Wound Model in Rats
- PMID: 26473072
- PMCID: PMC4601203
- DOI: 10.5812/ircmj.19960
Wound Healing Activity of a Traditionally Used Poly Herbal Product in a Burn Wound Model in Rats
Abstract
Background: Burns are known as one of the most common and destructive forms of injury with a vast spectrum of consequences. Despite the discovery of various antibacterial and antiseptic agents, burn wound healing still has remained a challenge to modern medicine. Plants, with a valuable traditional support, have been considered as potential agents for prevention and treatment of disorders in recent years. However, modern scientific methods should be applied to validate the claims about the therapeutic effects of the herbal products.
Objectives: This study was conducted to evaluate the wound-healing activity of a poly herbal cream (PHC), retrieved from Iranian Traditional Medicine (ITM), in a rat burn wound model in Iran.
Materials and methods: In this experimental study, PHC containing aqueous extracts of Malva sylvestris and Solanum nigrum leaves and oily extract of Rosa damascena petals was used. Second-degree burn wounds were induced in four groups of five rats each. Group 1 received no treatment while groups 2, 3 and 4 were given cream base, silver sulfadiazine (SS) 1% and PHC, respectively to compare the efficacy of PHC with the negative and positive control groups. The percentage of wound healing on days 2, 6, 10 and 14 and histopathological parameters of healed wounds on the 14th day were assessed. Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of PHC were evaluated using 2, 2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) and micro-dilution methods, respectively.
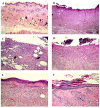
Results: There was a significant improvement in healing percentage of PHC-treated rats in comparison to the other groups at the end of the treatment period (87.0% ± 2.1% for PHC in comparison to 32.2% ± 1.6%, 57.0% ± 5.3% and 70.8% ± 3.5% for the control, cream base and SS groups, respectively). Moreover, the healed wounds in PHC-treated animals contained less inflammatory cells and had desirable re-epithelialization with remarkable neovascularization. In addition to the antioxidant activity, PHC exhibited antibacterial effect against Staphylococcus aureus.
Conclusions: Poly herbal cream experimentally and histopathologically revealed a burn wound healing activity probably due to the antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial activities of its phytochemical contents. Therefore, this study confirms the use of M. sylvestris, S. nigrum and R. damascena in burn prescriptions in ITM.
Keywords: Burn Wound Healing; Iranian Traditional Medicine (ITM); Malva sylvestris; Rosa damascena; Solanum nigrum.
Figures
References
-
- Ezzati A, Bayat M, Taheri S, Mohsenifar Z. Low-level laser therapy with pulsed infrared laser accelerates third-degree burn healing process in rats. J Rehabil Res Dev. 2009;46(4):543–54. - PubMed
-
- Khorasani G, Hosseinimehr SJ, Zamani P, Ghasemi M, Ahmadi A. The effect of saffron(Crocus sativus) extract for healing of second-degree burn wounds in rats. Keio J Med. 2008;57(4):190–5. - PubMed
-
- Avicenna.. The Canon of Medicine. Beirut: Institute of Al-A'lami Li Al-Matbooat; 2005.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
