Statin Use Is Associated with Reduced Mortality in Patients with Interstitial Lung Disease
- PMID: 26473476
- PMCID: PMC4608706
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140571
Statin Use Is Associated with Reduced Mortality in Patients with Interstitial Lung Disease
Abstract
Introduction: We hypothesized that statin use begun before the diagnosis of interstitial lung disease is associated with reduced mortality.
Methods: We studied all patients diagnosed with interstitial lung disease in the entire Danish population from 1995 through 2009, comparing statin use versus no statin use in a nested 1:2 matched study.
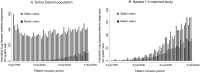
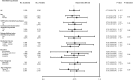
Results: The cumulative survival as a function of follow-up time from the date of diagnosis of interstitial lung disease (n = 1,786 + 3,572) and idiopathic lung fibrosis (n = 261 + 522) was higher for statin users versus never users (log-rank: P = 7 · 10(-9) and P = 0.05). The median survival time in patients with interstitial lung disease was 3.3 years in statin users and 2.1 years in never users. Corresponding values in patients with idiopathic lung fibrosis were 3.4 versus 2.4 years. After multivariable adjustment, the hazard ratio for all-cause mortality for statin users versus never users was 0.73 (95% confidence interval, 0.68 to 0.79) in patients with interstitial lung disease and 0.76 (0.62 to 0.93) in patients with idiopathic lung fibrosis. Results were robust in all sensitivity analyses.
Conclusion: Among patients with interstitial lung disease statin use was associated with reduced all-cause mortality.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Bradley B, Branley HM, Egan JJ, Greaves MS, Hansell DM, Harrison NK et al. Interstitial lung disease guideline: the British Thoracic Society in collaboration with the Thoracic Society of Australia and New Zealand and the Irish Thoracic Society. Thorax. 2008;63 Suppl 5: v1–58. 10.1136/thx.2008.101691 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bjoraker JA, Ryu JH, Edwin MK, Myers JL, Tazelaar HD, Schroeder DR et al. Prognostic significance of histopathologic subsets in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998;157: 199–203. - PubMed
-
- Goldstein JL, Brown MS Regulation of the mevalonate pathway. Nature. 1990;343: 425–430. - PubMed
-
- Van AL, D'Souza-Schorey C. Rho GTPases and signaling networks. Genes Dev. 1997;11: 2295–2322. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

