Acidosis-Induced Dysfunction of Cortical GABAergic Neurons through Astrocyte-Related Excitotoxicity
- PMID: 26474076
- PMCID: PMC4608795
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140324
Acidosis-Induced Dysfunction of Cortical GABAergic Neurons through Astrocyte-Related Excitotoxicity
Abstract
Background: Acidosis impairs cognitions and behaviors presumably by acidification-induced changes in neuronal metabolism. Cortical GABAergic neurons are vulnerable to pathological factors and their injury leads to brain dysfunction. How acidosis induces GABAergic neuron injury remains elusive. As the glia cells and neurons interact each other, we intend to examine the role of the astrocytes in acidosis-induced GABAergic neuron injury.
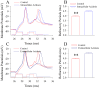
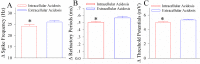
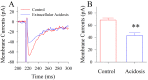
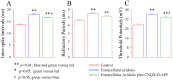
Results: Experiments were done at GABAergic cells and astrocytes in mouse cortical slices. To identify astrocytic involvement in acidosis-induced impairment, we induced the acidification in single GABAergic neuron by infusing proton intracellularly or in both neurons and astrocytes by using proton extracellularly. Compared the effects of intracellular acidification and extracellular acidification on GABAergic neurons, we found that their active intrinsic properties and synaptic outputs appeared more severely impaired in extracellular acidosis than intracellular acidosis. Meanwhile, extracellular acidosis deteriorated glutamate transporter currents on the astrocytes and upregulated excitatory synaptic transmission on the GABAergic neurons. Moreover, the antagonists of glutamate NMDA-/AMPA-receptors partially reverse extracellular acidosis-induced injury in the GABAergic neurons.
Conclusion: Our studies suggest that acidosis leads to the dysfunction of cortical GABAergic neurons by astrocyte-mediated excitotoxicity, in addition to their metabolic changes as indicated previously.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





References
-
- DuBose TD. Acidosis and Alkalosis Fauci AS, editor. New York: McGraw-Hill; 1997.
-
- Okuda T, Kurokawa K, Papadakis MA. Fluid and Electrolyte Disorders In: Tierney LM, McPhee SJ, Papadakis MA, editors. Current Medical Diagnosis & Treatment. 37th ed. Stamford: Appleton & Lange; 1998. p. 824–49.
-
- Nowak TJ, Handford AG. Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalances In: Nowak TJ, Handford AG, editors. Pathophysiology. third ed. Boston: Martin J. Lange; 2004. p. 422–45.
-
- Tizianello A, De Ferrari G, Gurreri G, Acquarone N. Effects of metabolic alkalosis, metabolic acidosis and uraemia on whole-body intracellular pH in man. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1977;52(2):125–35. Epub 1977/02/01. . - PubMed
-
- Rehncrona S. Brain acidosis. Ann Emerg Med. 1985;14(8):770–6. Epub 1985/08/01. doi: S0196-0644(85)80055-X [pii]. . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

