Ligand-based chemoinformatic discovery of a novel small molecule inhibitor targeting CDC25 dual specificity phosphatases and displaying in vitro efficacy against melanoma cells
- PMID: 26474275
- PMCID: PMC4741889
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.5473
Ligand-based chemoinformatic discovery of a novel small molecule inhibitor targeting CDC25 dual specificity phosphatases and displaying in vitro efficacy against melanoma cells
Abstract
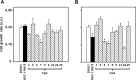
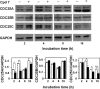
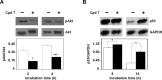
CDC25 phosphatases are important regulators of the cell cycle and represent promising targets for anticancer drug discovery. We recently identified NSC 119915 as a new quinonoid CDC25 inhibitor with potent anticancer activity. In order to discover more active analogs of NSC 119915, we performed a range of ligand-based chemoinformatic methods against the full ZINC drug-like subset and the NCI lead-like set. Nine compounds (3, 5-9, 21, 24, and 25) were identified with Ki values for CDC25A, -B and -C ranging from 0.01 to 4.4 μM. One of these analogs, 7, showed a high antiproliferative effect on human melanoma cell lines, A2058 and SAN. Compound 7 arrested melanoma cells in G2/M, causing a reduction of the protein levels of CDC25A and, more consistently, of CDC25C. Furthermore, an intrinsic apoptotic pathway was induced, which was mediated by ROS, because it was reverted in the presence of antioxidant N-acetyl-cysteine (NAC). Finally, 7 decreased the protein levels of phosphorylated Akt and increased those of p53, thus contributing to the regulation of chemosensitivity through the control of downstream Akt pathways in melanoma cells. Taken together, our data emphasize that CDC25 could be considered as a possible oncotarget in melanoma cells and that compound 7 is a small molecule CDC25 inhibitor that merits to be further evaluated as a chemotherapeutic agent for melanoma, likely in combination with other therapeutic compounds.
Keywords: CDC25 phosphatases; cancer; cell cycle; drug discovery; melanoma cells.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have a financial interest to declare.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Discovery and characterization of novel imidazopyridine derivative CHEQ-2 as a potent CDC25 inhibitor and promising anticancer drug candidate.Eur J Med Chem. 2014 Jul 23;82:293-307. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.05.063. Epub 2014 May 27. Eur J Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 24922544
-
Identification of highly potent and selective Cdc25 protein phosphatases inhibitors from miniaturization click-chemistry-based combinatorial libraries.Eur J Med Chem. 2019 Dec 1;183:111696. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.111696. Epub 2019 Sep 14. Eur J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 31541869
-
Benzyl isothiocyanate (BITC) induces G2/M phase arrest and apoptosis in human melanoma A375.S2 cells through reactive oxygen species (ROS) and both mitochondria-dependent and death receptor-mediated multiple signaling pathways.J Agric Food Chem. 2012 Jan 18;60(2):665-75. doi: 10.1021/jf204193v. Epub 2012 Jan 6. J Agric Food Chem. 2012. PMID: 22148415
-
Therapeutic targeting the cell division cycle 25 (CDC25) phosphatases in human acute myeloid leukemia--the possibility to target several kinases through inhibition of the various CDC25 isoforms.Molecules. 2014 Nov 12;19(11):18414-47. doi: 10.3390/molecules191118414. Molecules. 2014. PMID: 25397735 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CDC25A and B dual-specificity phosphatase inhibitors: potential agents for cancer therapy.Curr Med Chem. 2009;16(15):1831-49. doi: 10.2174/092986709788186084. Curr Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 19442149 Review.
Cited by
-
IBTK contributes to B-cell lymphomagenesis in Eμ-myc transgenic mice conferring resistance to apoptosis.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Apr 11;10(4):320. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1557-6. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 30975981 Free PMC article.
-
Cumingianoside A, a Phyto-Triterpenoid Saponin Inhibits Acquired BRAF Inhibitor Resistant Melanoma Growth via Programmed Cell Death.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Jan 28;10:30. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00030. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30745871 Free PMC article.
-
Advancements in mitochondrial-targeted nanotherapeutics: overcoming biological obstacles and optimizing drug delivery.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 17;15:1451989. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1451989. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39483479 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Silico Identification of Small Molecules as New Cdc25 Inhibitors through the Correlation between Chemosensitivity and Protein Expression Pattern.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 2;22(7):3714. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073714. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33918281 Free PMC article.
-
Oncogenic Tyrosine Phosphatases: Novel Therapeutic Targets for Melanoma Treatment.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Sep 29;12(10):2799. doi: 10.3390/cancers12102799. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33003469 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Russell P, Nurse P. cdc25+ functions as an inducer in the mitotic control of fission yeast. Cell. 1986;45:145–153. - PubMed
-
- Strausfeld U, Labbé JC, Fesquet D, Cavadore JC, Picard A, Sadhu K, Russell P, Dorée M. Dephosphorylation and activation of a p34cdc2/cyclin B complex in vitro by human CDC25 protein. Nature. 1991;351:242–245. - PubMed
-
- Karlsson-Rosenthal C, Millar JB. Cdc25: mechanisms of checkpoint inhibition and recovery. Trends Cell Biol. 2006;16:285–292. - PubMed
-
- Terada Y, Tatsuka M, Jinno S, Okayama H. Requirement for tyrosine phosphorylation of Cdk4 in G1 arrest induced by ultraviolet irradiation. Nature. 1995;376:358–362. - PubMed
-
- Iavarone A, Massague J. Repression of the CDK activator Cdc25A and cell-cycle arrest by cytokine TGF-beta in cells lacking the CDK inhibitor p15. Nature. 1997;387:417–422. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

