Risk Factors for Targeted Fungal and Mycobacterial Infections in Patients Taking Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitors
- PMID: 26474379
- PMCID: PMC5548176
- DOI: 10.1002/art.39468
Risk Factors for Targeted Fungal and Mycobacterial Infections in Patients Taking Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitors
Abstract
Objective: To identify predictors of the receipt of medical care, including the receipt of pre-drug screening, for diagnostically targeted fungal or mycobacterial infections among patients prescribed a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor (TNFi).
Methods: We conducted a case-control study using deidentified patient health claims information from a data set representing a commercially insured US population of 15 million patients annually from January 1, 2007 to December 31, 2009. Descriptive statistics as well as a 2-sample t-test, chi-square test of association, Fisher's exact test, and multivariate logistic regression were used for data analysis.
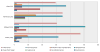
Results: A total of 30,772 patients received a TNFi during the study period. Of these, 158 patients (0.51%) developed targeted fungal and/or mycobacterial infections (cases). The median number of infections per case was 1.0 (interquartile range 1.0-2.0). Tuberculosis was diagnosed in 61% of cases, followed by histoplasmosis in 60%, nontuberculous mycobacterial infections in 11%, coccidioidomycosis in 10%, unspecified fungal infection in 8%, blastomycosis in 4%, cryptococcal infection in 3%, and pneumocystosis in 2%. Compared to controls (n = 474), a higher proportion of cases were prescribed prednisone (55% versus 37%; P < 0.001). Patients who were prescribed prednisone during the study period were twice as likely as those not taking prednisone to seek medical care attributable to a targeted fungal or mycobacterial infection (odds ratio 2.03; P < 0.001).
Conclusion: Development of a targeted fungal or mycobacterial infection among patients taking a TNFi is rare. Concomitant use of prednisone predicted development of such infections.
© 2016, American College of Rheumatology.
Figures

References
-
- American College of Rheumatology. Anti-TNF. 2012 https://www.rheumatology.org/Practice/Clinical/Patients/Medications/Anti...
-
- Chirch LM, Cataline PR, Dieckhaus KD, Grant-Kels JM. Proactive infectious disease approach to dermatologic patients who are taking tumor necrosis factor–alfa antagonists: Part II. Screening for patients on tumor necrosis factor–alfa antagonists. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71:11.e1–7. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. TB: data and statistics. 2014 http://www.cdc.gov/tb/statistics/default.htm.
-
- Van der Have M, Oldenburg B, Fidder HH, Belderbos TD, Siersema PD, van Oijen MG. Optimizing screening for tuberculosis and hepatitis B prior to starting tumor necrosis factor-α inhibitors in Crohn’s disease. Dig Dis Sci. 2014;59:554–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

