A GntR family transcription factor positively regulates mycobacterial isoniazid resistance by controlling the expression of a putative permease
- PMID: 26474554
- PMCID: PMC4609117
- DOI: 10.1186/s12866-015-0556-8
A GntR family transcription factor positively regulates mycobacterial isoniazid resistance by controlling the expression of a putative permease
Abstract
Background: Bacteria use transcriptional regulation to respond to environmental stresses. Specifically, exposure to antibacterial drugs is deemed to be an atypical stress, and altering transcriptional regulation in response to such stress can increase bacterial drug resistance. However, only a few transcription factors that regulate drug resistance have been reported.
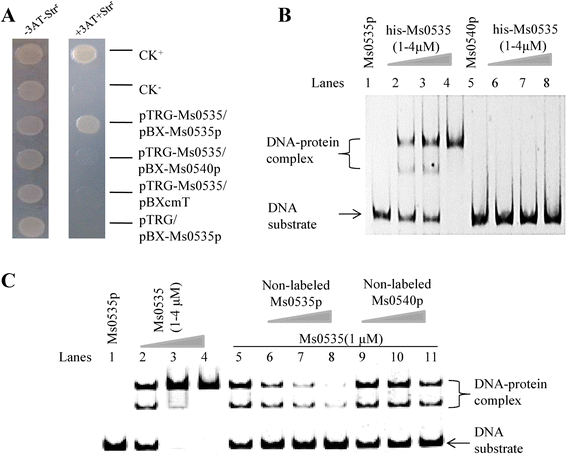
Results: In the present study, a GntR family transcription factor, encoded by the MSMEG_0535 (Ms0535) gene, was shown to be an isoniazid (INH) resistance regulator in Mycobacterium smegmatis. When the Ms0535 gene was overexpressed, cells showed a significant increase in INH resistance. First, the interaction between Ms0535 and its own promoter was determined, and a conserved 26-bp palindromic DNA binding motif was identified using electrophoretic mobility shift and DNaseI footprinting assays. Second, quantitative reverse transcription-PCR assays showed that Ms0535 acted as a transcriptional activator, and positively regulated its own expression, as well as that of a permease encoded by the MSMEG_0534 (Ms0534) gene. Similar to the case for the Ms0535 gene, a recombinant Ms0534-overexpressing strain also exhibited increased INH resistance compared with the wild-type strain. Furthermore, we showed that Ms0535 and Ms0534 deletion strains were more sensitive to INH than the wild-type strain. Interestingly, overexpressing Ms0534 in the Ms0535 deletion strain enhanced its INH resistance. In contrast, the Ms0534 deletion strain was still sensitive to INH even when Ms0535 was overexpressed. These findings suggest that Ms0534 is an effector protein that affects INH resistance in M. smegmatis.
Conclusions: In summary, the GntR transcriptional regulator Ms0535 positively regulates INH resistance by transcriptionally regulating the expression of the Ms0534 permease in M. smegmatis. These results improve our understanding of the role of transcriptional regulation in INH drug resistance in mycobacteria.
Figures





Similar articles
-
AraR, an L-Arabinose-Responding Transcription Factor, Negatively Regulates Resistance of Mycobacterium smegmatis to Isoniazid.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2019 May;84(5):540-552. doi: 10.1134/S0006297919050080. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2019. PMID: 31234768
-
Functional Characterization of Sirtuin-like Protein in Mycobacterium smegmatis.J Proteome Res. 2015 Nov 6;14(11):4441-9. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.5b00359. Epub 2015 Sep 29. J Proteome Res. 2015. PMID: 26375486
-
OxiR specifically responds to isoniazid and regulates isoniazid susceptibility in mycobacteria.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2019 May 1;366(10):fnz109. doi: 10.1093/femsle/fnz109. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31125044
-
Inactivation of the organic hydroperoxide stress resistance regulator OhrR enhances resistance to oxidative stress and isoniazid in Mycobacterium smegmatis.J Bacteriol. 2015 Jan 1;197(1):51-62. doi: 10.1128/JB.02252-14. Epub 2014 Oct 13. J Bacteriol. 2015. PMID: 25313389 Free PMC article.
-
Mycobacterium Lrp/AsnC family transcriptional factor modulates the arginase pathway as both a sensor and a transcriptional repressor.J Genet Genomics. 2021 Nov 20;48(11):1020-1031. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2021.06.018. Epub 2021 Jul 29. J Genet Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34696992 Review.
Cited by
-
Investigating a putative transcriptional regulatory protein encoded by Rv1719 gene of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Protein J. 2022 Jun;41(3):424-433. doi: 10.1007/s10930-022-10062-9. Epub 2022 Jun 17. Protein J. 2022. PMID: 35715720
-
Transcriptional regulator-induced phenotype screen reveals drug potentiators in Mycobacterium tuberculosis.Nat Microbiol. 2021 Jan;6(1):44-50. doi: 10.1038/s41564-020-00810-x. Epub 2020 Nov 16. Nat Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33199862 Free PMC article.
-
Antitoxin MqsA decreases antibiotic susceptibility through the global regulator AgtR in Pseudomonas fluorescens.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2023 Nov 15;67(11):e0081223. doi: 10.1128/aac.00812-23. Epub 2023 Oct 25. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2023. PMID: 37877694 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanism of the synergistic activity of ethambutol and isoniazid against Mycobacterium tuberculosis.J Biol Chem. 2018 Oct 26;293(43):16741-16750. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.002693. Epub 2018 Sep 5. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30185616 Free PMC article.
-
Citrate lyase CitE in Mycobacterium tuberculosis contributes to mycobacterial survival under hypoxic conditions.PLoS One. 2020 Apr 17;15(4):e0230786. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0230786. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32302313 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

