Genetic and nutrient modulation of acetyl-CoA levels in Synechocystis for n-butanol production
- PMID: 26474754
- PMCID: PMC4609045
- DOI: 10.1186/s12934-015-0355-9
Genetic and nutrient modulation of acetyl-CoA levels in Synechocystis for n-butanol production
Abstract
Background: There is a strong interest in using photosynthetic cyanobacteria as production hosts for biofuels and chemicals. Recent work has shown the benefit of pathway engineering, enzyme tolerance, and co-factor usage for improving yields of fermentation products.
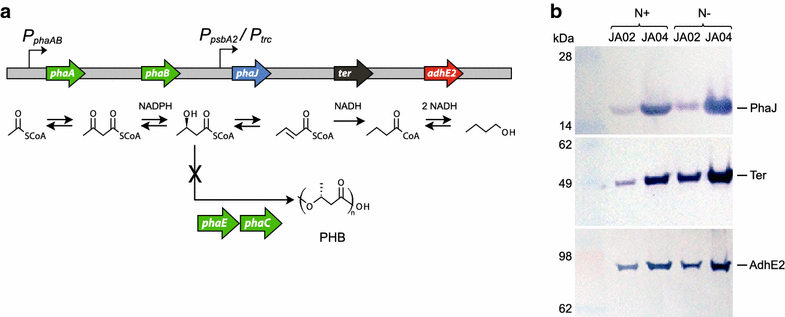
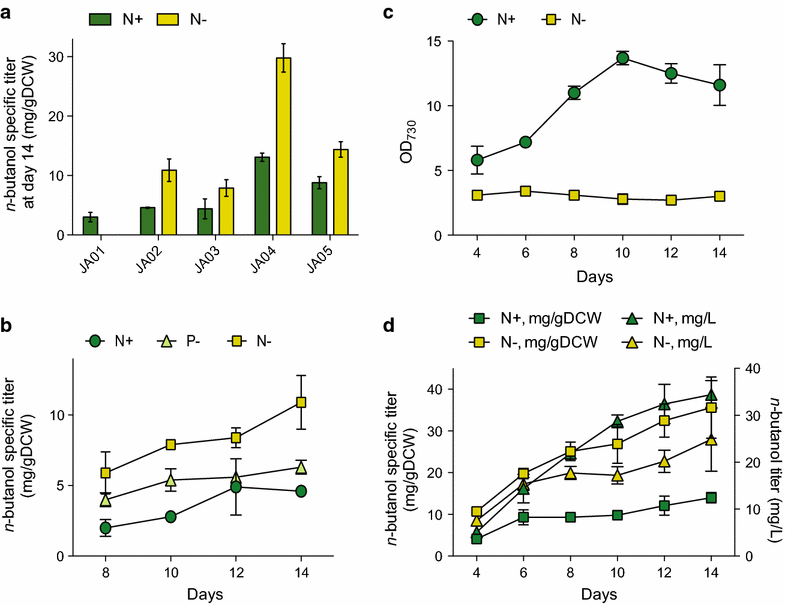
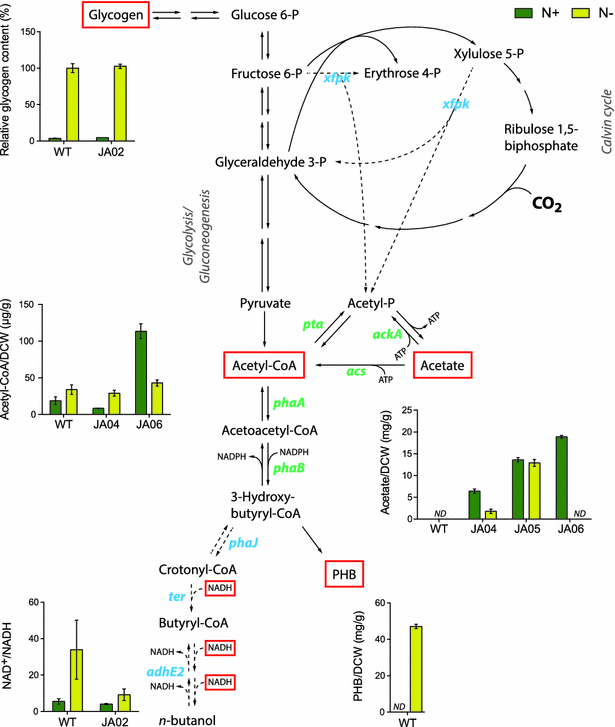
Results: An n-butanol pathway was inserted into a Synechocystis mutant deficient in polyhydroxybutyrate synthesis. We found that nitrogen starvation increased specific butanol productivity up to threefold, but cessation of cell growth limited total n-butanol titers. Metabolite profiling showed that acetyl-CoA increased twofold during nitrogen starvation. Introduction of a phosphoketolase increased acetyl-CoA levels sixfold at nitrogen replete conditions and increased butanol titers from 22 to 37 mg/L at day 8. Flux balance analysis of photoautotrophic metabolism showed that a Calvin-Benson-Bassham-Phosphoketolase pathway had higher theoretical butanol productivity than CBB-Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas and a reduced butanol ATP demand.
Conclusion: These results demonstrate that phosphoketolase overexpression and modulation of nitrogen levels are two attractive routes toward increased production of acetyl-CoA derived products in cyanobacteria and could be implemented with complementary metabolic engineering strategies.
Figures


References
-
- Lan EI, Ro SY, Liao JC. Oxygen-tolerant coenzyme A-acylating aldehyde dehydrogenase facilitates efficient photosynthetic n-butanol biosynthesis in cyanobacteria. Energy Environ Sci. 2013;6:2672–2681. doi: 10.1039/c3ee41405a. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

