The H1 linker histones: multifunctional proteins beyond the nucleosomal core particle
- PMID: 26474902
- PMCID: PMC4641498
- DOI: 10.15252/embr.201540749
The H1 linker histones: multifunctional proteins beyond the nucleosomal core particle
Abstract
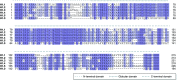
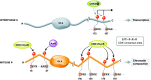
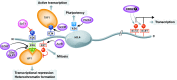
The linker histone H1 family members are a key component of chromatin and bind to the nucleosomal core particle around the DNA entry and exit sites. H1 can stabilize both nucleosome structure and higher-order chromatin architecture. In general, H1 molecules consist of a central globular domain with more flexible tail regions at both their N- and C-terminal ends. The existence of multiple H1 subtypes and a large variety of posttranslational modifications brings about a considerable degree of complexity and makes studying this protein family challenging. Here, we review recent progress in understanding the function of linker histones and their subtypes beyond their role as merely structural chromatin components. We summarize current findings on the role of H1 in heterochromatin formation, transcriptional regulation and embryogenesis with a focus on H1 subtypes and their specific modifications.
Keywords: chromatin; epigenetics; linker histone; modifications; subtypes.
© 2015 The Authors.
Figures

References
-
- Luger K, Mäder AW, Richmond RK, Sargent DF, Richmond TJ. Crystal structure of the nucleosome core particle at 2.8 A resolution. Nature. 1997;389:251–260. - PubMed
-
- Woodcock CL, Skoultchi AI, Fan Y. Role of linker histone in chromatin structure and function: H1 stoichiometry and nucleosome repeat length. Chromosome Res. 2006;14:17–25. - PubMed
-
- Robinson PJ, Rhodes D. Structure of the “30 nm” chromatin fibre: a key role for the linker histone. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2006;16:336–343. - PubMed
-
- Schlissel MS, Brown DD. The transcriptional regulation of Xenopus 5s RNA genes in chromatin: the roles of active stable transcription complexes and histone H1. Cell. 1984;37:903–913. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

