5-Hydroxytryptamine promotes hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation by influencing β-catenin
- PMID: 26474915
- PMCID: PMC5528951
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molonc.2015.09.008
5-Hydroxytryptamine promotes hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation by influencing β-catenin
Abstract
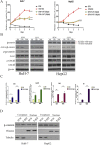
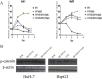
5-Hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), a neurotransmitter and vasoactive factor, has been reported to promote proliferation of serum-deprived hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells but the detailed intracellular mechanism is unknown. As Wnt/β-catenin signalling is highly dysregulated in a majority of HCC, this study explored the regulation of Wnt/β-catenin signalling by 5-HT. The expression of various 5-HT receptors was studied by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) in HCC cell lines as well as in 33 pairs of HCC tumours and corresponding adjacent non-tumour tissues. Receptors 5-HT1D (21/33, 63.6%), 5-HT2B (12/33, 36.4%) and 5-HT7 (15/33, 45.4%) were overexpressed whereas receptors 5-HT2A (17/33, 51.5%) and 5-HT5 (30/33, 90.1%) were reduced in HCC tumour tissues. In vitro data suggests 5-HT increased total β-catenin, active β-catenin and decreased phosphorylated β-catenin protein levels in serum deprived HuH-7 and HepG2 cells compared to control cells under serum free medium without 5-HT. Activation of Wnt/β-catenin signalling was evidenced by increased expression of β-catenin downstream target genes, Axin2, cyclin D1, dickoppf-1 (DKK1) and glutamine synthetase (GS) by qPCR in serum-deprived HCC cell lines treated with 5-HT. Additionally, biochemical analysis revealed 5-HT disrupted Axin1/β-catenin interaction, a critical step in β-catenin phosphorylation. Increased Wnt/β-catenin activity was attenuated by antagonist of receptor 5-HT7 (SB-258719) in HCC cell lines and patient-derived primary tumour tissues in the presence of 5-HT. SB-258719 also reduced tumour growth in vivo. This study provides evidence of Wnt/β-catenin signalling activation by 5-HT and may represent a potential therapeutic target for hepatocarcinogenesis.
Keywords: 5-HT; SB-258719; Wnt/β-catenin signalling.
Copyright © 2015 Federation of European Biochemical Societies. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Beyer, T. , Danilchik, M. , Thumberger, T. , Vick, P. , Tisler, M. , Schneider, I. , Bogusch, S. , Andre, P. , Ulmer, B. , Walentek, P. , Niesler, B. , Blum, M. , Schweickert, A. , 2012. Serotonin signaling is required for Wnt-dependent GRP specification and leftward flow in Xenopus. Curr. Biol. 22, 33–39. - PubMed
-
- Cadoret, A. , Ovejero, C. , Terris, B. , Souil, E. , Levy, L. , Lamers, W.H. , Kitajewski, J. , Kahn, A. , Perret, C. , 2002. New targets of beta-catenin signaling in the liver are involved in the glutamine metabolism. Oncogene. 21, 8293–8301. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

