GABA-induced inactivation of dorsal midline thalamic subregions has distinct effects on emotional behaviors
- PMID: 26475506
- PMCID: PMC4679604
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2015.10.029
GABA-induced inactivation of dorsal midline thalamic subregions has distinct effects on emotional behaviors
Abstract
The paraventricular nucleus of the thalamus (PVT) is a key node integrating information about emotion and relaying output to other limbic structures influencing motor behavior. With recent studies showing the anterior (aPVT) and posterior (pPVT) subregions of this nucleus to have different anatomical connections and functions in ingestive behavior, the present study investigated whether they also make different contributions to emotional behaviors. Rats were microinjected in the aPVT or pPVT with saline vehicle or the GABAB+GABAA agonists, baclofen+muscimol (bac+mus; 0.3+0.03nmol), to inhibit neural activity and were then tested between-subject for differences in emotional behavior. In a novel activity chamber, bac+mus significantly reduced locomotor activity, with this change somewhat larger after injection in the pPVT than the aPVT. In a familiar activity chamber, bac+mus again reduced locomotor activity but induced similar changes after injection in the aPVT and pPVT. In an elevated plus maze, bac+mus significantly decreased open arm time and entries, although this was observed only after injection in the pPVT. Thus, while both PVT subregions are necessary for general locomotor activity, the pPVT appears to have a greater function in both novelty-induced activity and anxiety-like behavior, indicating that this subregion makes a greater contribution than the aPVT to reactions to stressful stimuli.
Keywords: Baclofen; Elevated plus maze; Locomotor activity; Muscimol; Novelty; Paraventricular nucleus of the thalamus.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

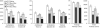


References
-
- Arcelli P, Frassoni C, Regondi MC, De Biasi S, Spreafico R. GABAergic neurons in mammalian thalamus: a marker of thalamic complexity? Brain research bulletin. 1997;42:27–37. - PubMed
-
- Bhatnagar S, Dallman M. Neuroanatomical basis for facilitation of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal responses to a novel stressor after chronic stress. Neuroscience. 1998;84:1025–1039. - PubMed
-
- Bischoff S, Leonhard S, Reymann N, Schuler V, Shigemoto R, Kaupmann K, Bettler B. Spatial distribution of GABA(B)R1 receptor mRNA and binding sites in the rat brain. The Journal of comparative neurology. 1999;412:1–16. - PubMed
-
- Bullitt E. Expression of c-fos-like protein as a marker for neuronal activity following noxious stimulation in the rat. The Journal of comparative neurology. 1990;296:517–530. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

