Assembly and Molecular Architecture of the Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase p85α Homodimer
- PMID: 26475863
- PMCID: PMC4683262
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.689604
Assembly and Molecular Architecture of the Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase p85α Homodimer
Abstract
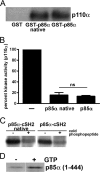
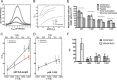
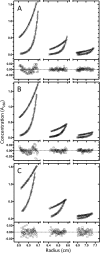
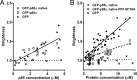
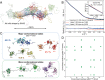
Phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3Ks) are a family of lipid kinases that are activated by growth factor and G-protein-coupled receptors and propagate intracellular signals for growth, survival, proliferation, and metabolism. p85α, a modular protein consisting of five domains, binds and inhibits the enzymatic activity of class IA PI3K catalytic subunits. Here, we describe the structural states of the p85α dimer, based on data from in vivo and in vitro solution characterization. Our in vitro assembly and structural analyses have been enabled by the creation of cysteine-free p85α that is functionally equivalent to native p85α. Analytical ultracentrifugation studies showed that p85α undergoes rapidly reversible monomer-dimer assembly that is highly exothermic in nature. In addition to the documented SH3-PR1 dimerization interaction, we identified a second intermolecular interaction mediated by cSH2 domains at the C-terminal end of the polypeptide. We have demonstrated in vivo concentration-dependent dimerization of p85α using fluorescence fluctuation spectroscopy. Finally, we have defined solution conditions under which the protein is predominantly monomeric or dimeric, providing the basis for small angle x-ray scattering and chemical cross-linking structural analysis of the discrete dimer. These experimental data have been used for the integrative structure determination of the p85α dimer. Our study provides new insight into the structure and assembly of the p85α homodimer and suggests that this protein is a highly dynamic molecule whose conformational flexibility allows it to transiently associate with multiple binding proteins.
Keywords: analytical ultracentrifugation; molecular modeling; phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase (PI 3-kinase); phosphatidylinositol signaling; small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS); structural model.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Burke J. E., and Williams R. L. (2015) Synergy in activating class I PI3Ks. Trends Biochem. Sci. 40, 88–100 - PubMed
-
- Maehama T., and Dixon J. E. (1998) The tumor suppressor, PTEN/MMAC1, dephosphorylates the lipid second messenger, phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 13375–13378 - PubMed
-
- Tolias K. F., Cantley L. C., and Carpenter C. L. (1995) Rho family GTPases bind to phosphoinositide kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 17656–17659 - PubMed
-
- Zheng Y., Bagrodia S., and Cerione R. A. (1994) Activation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase activity by Cdc42Hs binding to p85. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 18727–18730 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
- P01 CA100324/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS83085/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01GM112524/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK041296/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P41RR001209/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P41 GM103314/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR001209/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS083085/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM112524/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P41GM103393/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32GM007288/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007288/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA013330/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P41 GM103393/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

