Structures of the double-ring AAA ATPase Pex1-Pex6 involved in peroxisome biogenesis
- PMID: 26476099
- PMCID: PMC4803591
- DOI: 10.1111/febs.13569
Structures of the double-ring AAA ATPase Pex1-Pex6 involved in peroxisome biogenesis
Abstract
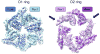
The Pex1 and Pex6 proteins are members of the AAA family of ATPases and are involved in peroxisome biogenesis. Recently, cryo-electron microscopy structures of the Pex1-Pex6 complex in different nucleotide states have been determined. This Structural Snapshot describes the structural features of the complex and their implications for its function, as well as questions that still await answers.
Keywords: AAA ATPases; Pex1-Pex6 complex; cryo-electron microscopy; peroxisome biogenesis; single-particle analysis.
© 2015 FEBS.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Insights into the Structure and Function of the Pex1/Pex6 AAA-ATPase in Peroxisome Homeostasis.Cells. 2022 Jun 29;11(13):2067. doi: 10.3390/cells11132067. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35805150 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Pex1/Pex6 complex is a heterohexameric AAA+ motor with alternating and highly coordinated subunits.J Mol Biol. 2015 Mar 27;427(6 Pt B):1375-1388. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2015.01.019. Epub 2015 Feb 7. J Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25659908 Free PMC article.
-
Unique double-ring structure of the peroxisomal Pex1/Pex6 ATPase complex revealed by cryo-electron microscopy.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Jul 28;112(30):E4017-25. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1500257112. Epub 2015 Jul 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 26170309 Free PMC article.
-
The peroxisomal AAA-ATPase Pex1/Pex6 unfolds substrates by processive threading.Nat Commun. 2018 Jan 10;9(1):135. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02474-4. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29321502 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Mapping of Missense Mutations in the Pex1/Pex6 Complex.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Aug 1;20(15):3756. doi: 10.3390/ijms20153756. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31374812 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Insights into the Structure and Function of the Pex1/Pex6 AAA-ATPase in Peroxisome Homeostasis.Cells. 2022 Jun 29;11(13):2067. doi: 10.3390/cells11132067. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35805150 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peroxisomal monoubiquitinated PEX5 interacts with the AAA ATPases PEX1 and PEX6 and is unfolded during its dislocation into the cytosol.J Biol Chem. 2018 Jul 20;293(29):11553-11563. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.003669. Epub 2018 Jun 8. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29884772 Free PMC article.
-
The peroxisome: an update on mysteries 3.0.Histochem Cell Biol. 2024 Feb;161(2):99-132. doi: 10.1007/s00418-023-02259-5. Epub 2024 Jan 20. Histochem Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38244103 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peroxisome biogenesis disorders.Transl Sci Rare Dis. 2016 Nov 7;1(2):111-144. doi: 10.3233/TRD-160003. Transl Sci Rare Dis. 2016. PMID: 29152457 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Structure of the peroxisomal Pex1/Pex6 ATPase complex bound to a substrate.Nat Commun. 2023 Sep 23;14(1):5942. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-41640-9. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37741838 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

