Selection of 2'-deoxy-2'-fluoroarabinonucleotide (FANA) aptamers that bind HIV-1 reverse transcriptase with picomolar affinity
- PMID: 26476448
- PMCID: PMC4751925
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkv1057
Selection of 2'-deoxy-2'-fluoroarabinonucleotide (FANA) aptamers that bind HIV-1 reverse transcriptase with picomolar affinity
Abstract
Using a Systematic Evolution of Ligands by Exponential Enrichment (SELEX) protocol capable of selecting xeno-nucleic acid (XNA) aptamers, a 2'-deoxy-2'-fluoroarabinonucleotide (FANA) aptamer (referred to as FA1) to HIV-1 reverse transcriptase (HIV-1 RT) was selected. FA1 bound HIV-1 RT with KD,app values in the low pM range under different ionic conditions. Comparisons to published HIV-1 RT RNA and DNA aptamers indicated that FA1 bound at least as well as these aptamers. FA1 contained a 20 nucleotide 5' DNA sequence followed by a 57 nucleotide region of FANA nucleotides. Removal of the fourteen 5' DNA nucleotides did not affect binding. FA1's predicted structure was composed of four stems and four loops. All stem nucleotides could be modified to G-C base pairs (14 total changes) with a small effect on binding. Eliminating or altering most loop sequences reduced or abolished tight binding. Overall, results suggested that the structure and the sequence of FA1 were important for binding. FA1 showed strong inhibition of HIV-1 RT in extension assays while no specific binding to avian myeloblastosis or Moloney murine leukemia RTs was detected. A complete DNA version of FA1 showed low binding to HIV-1 RT, emphasizing the unique properties of FANA in HIV-1 RT binding.
© The Author(s) 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures




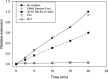
References
-
- Telesnitsky A., Goff S.P. In: Retroviruses. Coffin JM, Hughes SH, Varmus HE, editors. NY: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 1997. pp. 121–160. - PubMed
-
- Brody E.N., Gold L. Aptamers as therapeutic and diagnostic agents. J. Biotechnol. 2000;74:5–13. - PubMed
-
- Deisingh A.K. Aptamer-based biosensors: biomedical applications. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2006:341–357. - PubMed
-
- Gold L. The SELEX process: a surprising source of therapeutic and diagnostic compounds. Harvey Lect. 1995;91:47–57. - PubMed
-
- James W. Aptamers in the virologists’ toolkit. J. Gen. Virol. 2007;88:351–364. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

