Prognostic Value of VEGF in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Treated with Sorafenib: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 26476711
- PMCID: PMC4617189
- DOI: 10.12659/msm.894617
Prognostic Value of VEGF in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Treated with Sorafenib: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is characterized by rich vascularization in the tumor, and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) plays important roles in vascularization. The results of the roles of VEGF in predicting efficacy of sorafenib in HCC are conflicting. In this meta-analysis, we aimed to investigate the prognostic and predictive value of VEGF in HCC patients receiving sorafenib.
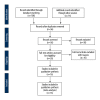
Material and methods: PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane library electronic databases were systematically searched for eligible studies. The baseline characteristics were recorded and overall qualities of the eligible studies were assessed by 2 reviewers independently. VEGF levels and data relevant to efficacy of sorafenib were extracted and used for meta-analysis.
Results: The comprehensive search yielded 9 studies that evaluated the relationship between VEGF level and clinical outcome in advanced HCC patients treated with sorafenib. Pooled estimates suggested that high level of VEGF was associated with poor overall survival (HR=1.85; 95% CI: 1.24-2.77; P=0.003) and poor progression-free survival (HR=2.09; 95% CI: 1.43-3.05; P<0.01) in HCC. Mutation of VEGF had a favorable effect on hand-foot skin reaction in HCC patients treated with sorafenib (P<0.05).
Conclusions: High level of VEGF is associated with poor outcomes in HCC patients treated with sorafenib, indicating that VEGF could be used as an indicator of clinical efficacy in patients with HCC. However, more well-designed studies are needed to strengthen our findings.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Changes in plasma vascular endothelial growth factor at 8 weeks after sorafenib administration as predictors of survival for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer. 2014 Jan 15;120(2):229-37. doi: 10.1002/cncr.28384. Epub 2013 Oct 7. Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24122122 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
VEGF and VEGFR genotyping in the prediction of clinical outcome for HCC patients receiving sorafenib: the ALICE-1 study.Int J Cancer. 2014 Sep 1;135(5):1247-56. doi: 10.1002/ijc.28772. Epub 2014 Feb 20. Int J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24510746
-
An updated meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials assessing the effect of sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 2;9(12):e112530. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112530. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25460347 Free PMC article.
-
Early predictive value of circulating biomarkers for sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2022 Mar;22(3):361-378. doi: 10.1080/14737159.2022.2049248. Epub 2022 Mar 11. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2022. PMID: 35234564 Review.
-
Case analysis of complete remission of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma achieved with sorafenib.Eur J Med Res. 2015 Feb 4;20(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s40001-015-0085-9. Eur J Med Res. 2015. PMID: 25649133 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Meta-Analysis of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor for Nasopharyngeal Cancer Prognosis.Front Oncol. 2018 Oct 31;8:486. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2018.00486. eCollection 2018. Front Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30430078 Free PMC article.
-
Platelets and Hepatocellular Cancer: Bridging the Bench to the Clinics.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Oct 15;11(10):1568. doi: 10.3390/cancers11101568. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31618961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Precision medicine for hepatocellular carcinoma: driver mutations and targeted therapy.Oncotarget. 2017 Jun 6;8(33):55715-55730. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18382. eCollection 2017 Aug 15. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28903454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aberrant angiogenic signaling in HCC: therapeutic targeting and drug resistance.Front Oncol. 2025 Jun 18;15:1595195. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1595195. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40606973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA Therapeutic Options to Manage Aberrant Signaling Pathways in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Dream or Reality?Front Oncol. 2022 May 4;12:891812. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.891812. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35600358 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hollebecque A, Malka D, Ferte C, et al. Systemic treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: from disillusions to new horizons. Eur J Cancer. 2015;51:327–39. - PubMed
-
- Sangro B. Evidence-based integration of selective internal radiation therapy into hepatocellular carcinoma management. Future Oncol. 2014;10:7–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

