Countdown to 2015: a decade of tracking progress for maternal, newborn, and child survival
- PMID: 26477328
- PMCID: PMC7613171
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00519-X
Countdown to 2015: a decade of tracking progress for maternal, newborn, and child survival
Erratum in
-
Department of Error.Lancet. 2016 May 14;387(10032):1998. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30471-8. Lancet. 2016. PMID: 27203773 No abstract available.
Abstract
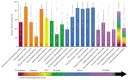
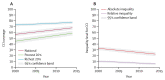
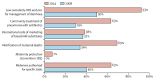
Conceived in 2003 and born in 2005 with the launch of its first report and country profiles, the Countdown to 2015 for Maternal, Newborn, and Child Survival has reached its originally proposed lifespan. Major reductions in the deaths of mothers and children have occurred since Countdown's inception, even though most of the 75 priority countries failed to achieve Millennium Development Goals 4 and 5. The coverage of life-saving interventions tracked in Countdown increased steadily over time, but wide inequalities persist between and within countries. Key drivers of coverage such as financing, human resources, commodities, and conducive health policies also showed important, yet insufficient increases. As a multistakeholder initiative of more than 40 academic, international, bilateral, and civil society institutions, Countdown was successful in monitoring progress and raising the visibility of the health of mothers, newborns, and children. Lessons learned from this initiative have direct bearing on monitoring progress during the Sustainable Development Goals era.
Copyright © 2016 World Health Organization. Published by Elsevier Ltd/Inc/BV. All rights reserved. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Claeson M, Gillespie D, Mshinda H, Troedsson H, Victora CG, the Bellagio Study Group on Child Survival Knowledge into action for child survival. Lancet. 2003;362:323–27. - PubMed
-
- Countdown to 2015. Tracking progress in child survival: the 2005 report. UNICEF; New York: 2005.
-
- Countdown to 2015. Tracking progress in maternal, neonatal and child survival: The 2008 report. UNICEF; New York: 2008.
-
- Countdown to 2015. Countdown to 2015 decade report (2000-2010): taking stock of maternal, newborn and child survival. UNICEF; New York: 2010. - PubMed
-
- Countdown to 2015. Building a future for women and children: the 2012 report. World Health Organization and UNICEF; Washington, DC: 2012.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

