Impact Of Environmental Variation On Host Performance Differs With Pathogen Identity: Implications For Host-Pathogen Interactions In A Changing Climate
- PMID: 26477393
- PMCID: PMC4609993
- DOI: 10.1038/srep15351
Impact Of Environmental Variation On Host Performance Differs With Pathogen Identity: Implications For Host-Pathogen Interactions In A Changing Climate
Abstract
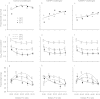
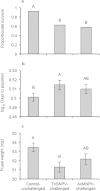
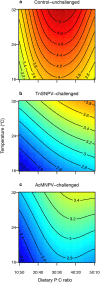
Specialist and generalist pathogens may exert different costs on their hosts; thereby altering the way hosts cope with environmental variation. We examined how pathogen-challenge alters the environmental conditions that maximize host performance by simultaneously varying temperature and nutrition (protein to carbohydrate ratio; P:C) after exposure to two baculoviruses; one that is specific to the cabbage looper, Trichoplusia ni (TnSNPV) and another that has a broad host range (AcMNPV). Virus-challenged larvae performed better on more protein-biased diets, primarily due to higher survival, whereas unchallenged larvae performed best on a balanced diet. The environmental conditions that maximized host performance differed with virus identity because TnSNPV-challenge inflicted fitness costs (reduced pupal weight and prolonged development) whereas AcMNPV-challenge did not. The performance of TnSNPV-challenged larvae rose with increasing P:C across all temperatures, whereas temperature modulated the optimal P:C in AcMNPV-challenged larvae (slightly protein-biased at 16 °C to increasingly higher P:C as temperature increased). Increasing temperature reduced pupal size, but only at more balanced P:C ratios, indicating that nutrition moderates the temperature-size rule. Our findings highlight the complex environmental interactions that can alter host performance after exposure to pathogens, which could impact the role of entomopathogens as regulators of insect populations in a changing climate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Altizer S., Ostfeld R. S., Johnson P. T. J., Kutz S. & Harvell C. D. Climate change and infectious diseases: from evidence to a predictive framework. Science. 341, 514–519 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Black R. E., Morris S. S. & Bryce J. Where and why are 10 million children dying every year? Lancet 361, 2226–2234 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Thomas M. B. & Blanford S. Thermal biology in insect-parasite interactions. Trends Ecol. Evol. 18, 344–350 (2003).
-
- Shikano I., Ericsson J. D., Cory J. S. & Myers J. H. Indirect plant-mediated effects on insect immunity and disease resistance in a tritrophic system. Basic Appl. Ecol. 11, 15–22 (2010).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

