Cloning of the short-tailed Gyeongju Donggyeong dog via SCNT: conserving phenotypic inheritance
- PMID: 26477541
- PMCID: PMC4785129
- DOI: 10.1292/jvms.15-0107
Cloning of the short-tailed Gyeongju Donggyeong dog via SCNT: conserving phenotypic inheritance
Abstract
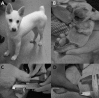
Somatic cell nuclear transfer is a useful tool to maintain genetic information of animals. The Gyeongju Donggyeong dog is a breed registered as natural monument in Korea. The unique feature of the Donggyeong dog is its tail, as the Donggyeong dog can be classified as either short tailed or tailless. The aim of this study was to preserve the Donggyeong dog's unique feature by cloning. Fibroblasts were obtained from a short-tailed Donggyeong dog. In vivo matured oocytes were enucleated, microinjected with a donor cell and fused electrically. Reconstructed embryos were transferred to six recipient dogs. One surrogate became pregnant, and one short-tailed Donggyeong dog was delivered. This study demonstrated that the phenotype of the Donggyeong dog could be conserved by somatic cell nuclear transfer.
Figures
References
-
- Choi S. G.2010. Studies on the origin and breed characteristics of Gyeongju Donggyeong dog. Ph.D. Dissertation. Daegu University, Korea.
-
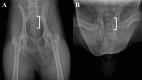
- Choi S. G., Sung K. C., Lee E. W.2010. Study on anatomical characteristics by radiographic evaluation of the coccyx and pelvis in the Gyeongju Donggyeong dogs. Korean J. Res. Gyeongju 19: 163–173.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

