Recent Advances and New Strategies in Targeting Plk1 for Anticancer Therapy
- PMID: 26478211
- PMCID: PMC4684765
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tips.2015.08.013
Recent Advances and New Strategies in Targeting Plk1 for Anticancer Therapy
Abstract
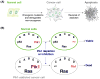
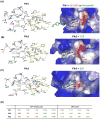
Polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1) plays key roles in regulating mitotic processes that are crucial for cellular proliferation. Overexpression of Plk1 is tightly associated with the development of particular cancers in humans, and a large body of evidence suggests that Plk1 is an attractive target for anticancer therapeutic development. Drugs targeting Plk1 can potentially be directed at two distinct sites: the N-terminal catalytic kinase domain (KD), which phosphorylates substrates, and the C-terminal polo-box domain (PBD) which is essential for protein-protein interactions. In this review we summarize recent advances and new challenges in the development of Plk1 inhibitors targeting these two domains. We also discuss novel strategies for designing and developing next-generation inhibitors to effectively treat Plk1-associated human disorders.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Plk1-targeted small molecule inhibitors: molecular basis for their potency and specificity.Mol Cells. 2011 Sep;32(3):209-20. doi: 10.1007/s10059-011-0126-3. Epub 2011 Jul 29. Mol Cells. 2011. PMID: 21809214 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polo-like Kinase 1 as an emerging drug target: structure, function and therapeutic implications.J Drug Target. 2021 Feb;29(2):168-184. doi: 10.1080/1061186X.2020.1818760. Epub 2020 Sep 14. J Drug Target. 2021. PMID: 32886539 Review.
-
Differential Cellular Effects of Plk1 Inhibitors Targeting the ATP-binding Domain or Polo-box Domain.J Cell Physiol. 2015 Dec;230(12):3057-67. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25042. J Cell Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25975351
-
Design and synthesis of a cell-permeable, drug-like small molecule inhibitor targeting the polo-box domain of polo-like kinase 1.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 11;9(9):e107432. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0107432. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25211362 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a Polo-like Kinase-1 Polo-Box Domain Inhibitor as a Tumor Growth Suppressor in Mice Models.J Med Chem. 2020 Dec 10;63(23):14905-14920. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c01451. Epub 2020 Nov 3. J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 33142063 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Identification of a Five-Gene Signature for Predicting Survival in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Patients.Front Genet. 2020 Aug 7;11:899. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00899. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 32849853 Free PMC article.
-
HILPS, a long noncoding RNA essential for global oxygen sensing in humans.Sci Adv. 2023 Nov 24;9(47):eadi1867. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adi1867. Epub 2023 Nov 22. Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 37992175 Free PMC article.
-
Unusually High Affinity of the PLK Inhibitors RO3280 and GSK461364 to HSA and Its Possible Pharmacokinetic Implications.Mol Pharm. 2023 Mar 6;20(3):1631-1642. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.2c00849. Epub 2023 Feb 22. Mol Pharm. 2023. PMID: 36812406 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Risk Score Model of Lactate Metabolism for Predicting over Survival and Immune Signature in Lung Adenocarcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jul 30;14(15):3727. doi: 10.3390/cancers14153727. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35954390 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Polo-like kinase 1 interaction inhibitors using a novel cell-based assay.Sci Rep. 2016 Nov 22;5:37581. doi: 10.1038/srep37581. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27874094 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hanks SK, et al. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988;241:42–52. - PubMed
-
- Lahiry P, et al. Kinase mutations in human disease: interpreting genotype–phenotype relationships. Nat Rev Genet. 2010;11:60–74. - PubMed
-
- Melnikova I, Golden J. Targeting protein kinases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2004;3:993–994. - PubMed
-
- Garuti L, et al. Polo-like kinases inhibitors. Curr Med Chem. 2012;19:3937–3948. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

