Inflammatory mechanisms of pulmonary injury induced by mustards
- PMID: 26478570
- PMCID: PMC4753082
- DOI: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2015.10.011
Inflammatory mechanisms of pulmonary injury induced by mustards
Abstract
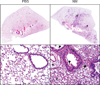
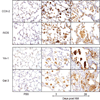
Exposure of humans and animals to vesicants, including sulfur mustard (SM) and nitrogen mustard (NM), causes severe and debilitating damage to the respiratory tract. Both acute and long term pathological consequences are observed in the lung following a single exposure to these vesicants. Evidence from our laboratories and others suggest that macrophages and the inflammatory mediators they release play an important role in mustard-induced lung injury. In this paper, the pathogenic effects of SM and NM on the lung are reviewed, along with the potential role of inflammatory macrophages and mediators they release in mustard-induced pulmonary toxicity.
Keywords: Lung injury; Pulmonary toxicity; TNFα; Vesicant; iNOS.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Aggarwal BB. Signalling pathways of the TNF superfamily: a double-edged sword. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003;3:745–756. - PubMed
-
- Aghanouri R, Ghanei M, Aslani J, Keivani-Amine H, Rastegar F, Karkhane A. Fibrogenic cytokine levels in bronchoalveolar lavage aspirates 15 years after exposure to sulfur mustard. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2004;287:L1160–L1164. - PubMed
-
- Anderson DR, Taylor SL, Fetterer DP, Holmes WW. Evaluation of protease inhibitors and an antioxidant for treatment of sulfur mustard-induced toxic lung injury. Toxicology. 2009;263:41–46. - PubMed
-
- Arafa HM, Abdel-Wahab MH, El-Shafeey MF, Badary OA, Hamada FM. Anti-fibrotic effect of meloxicam in a murine lung fibrosis model. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007;564:181–189. - PubMed
-
- Balali-Mood M, Hefazi M. The pharmacology, toxicology, and medical treatment of sulphur mustard poisoning. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2005;19:297–315. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

