Assembly of actin filaments and microtubules in Nwk F-BAR-induced membrane deformations
- PMID: 26478768
- PMCID: PMC4594231
- DOI: 10.1080/19420889.2014.1000703
Assembly of actin filaments and microtubules in Nwk F-BAR-induced membrane deformations
Abstract
F-BAR domains form crescent-shaped dimers that bind to and deform lipid bilayers, and play a role in many cellular processes requiring membrane remodeling, including endocytosis and cell morphogenesis. Nervous Wreck (NWK) encodes an F-BAR/SH3 protein that regulates synapse growth in Drosophila. Unlike conventional F-BAR proteins that assemble tip-to-tip into filaments and helical arrays around membrane tubules, the Nwk F-BAR domain instead assembles into zigzags, creating ridges and periodic scallops on membranes in vitro. In cells, this membrane deforming activity generates small buds, which can lengthen into extensive protrusions upon actin cytoskeleton polymerization. Here, we show that Nwk-induced cellular protrusions contain dynamic microtubules, distinguishing them from conventional filopodia, and further do not depend on actin filaments or microtubules for their maintenance. Our results indicate new ways in which close cooperation between the membrane remodeling and cytoskeletal machinery underlies large-scale changes in cellular morphology.
Keywords: F-BAR; Nwk; actin; membrane; microtubule.
Figures
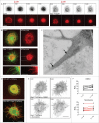
Similar articles
-
Membrane Charge Directs the Outcome of F-BAR Domain Lipid Binding and Autoregulation.Cell Rep. 2015 Dec 22;13(11):2597-2609. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.11.044. Epub 2015 Dec 10. Cell Rep. 2015. PMID: 26686642 Free PMC article.
-
Formation of membrane ridges and scallops by the F-BAR protein Nervous Wreck.Mol Biol Cell. 2013 Aug;24(15):2406-18. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E13-05-0271. Epub 2013 Jun 12. Mol Biol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23761074 Free PMC article.
-
Coordinated autoinhibition of F-BAR domain membrane binding and WASp activation by Nervous Wreck.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Sep 20;113(38):E5552-61. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1524412113. Epub 2016 Sep 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27601635 Free PMC article.
-
BAR domain proteins-a linkage between cellular membranes, signaling pathways, and the actin cytoskeleton.Biophys Rev. 2018 Dec;10(6):1587-1604. doi: 10.1007/s12551-018-0467-7. Epub 2018 Nov 19. Biophys Rev. 2018. PMID: 30456600 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Higher-order assemblies of BAR domain proteins for shaping membranes.Microscopy (Oxf). 2016 Jun;65(3):201-10. doi: 10.1093/jmicro/dfw002. Epub 2016 Feb 15. Microscopy (Oxf). 2016. PMID: 26884618 Review.
Cited by
-
Membrane Charge Directs the Outcome of F-BAR Domain Lipid Binding and Autoregulation.Cell Rep. 2015 Dec 22;13(11):2597-2609. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.11.044. Epub 2015 Dec 10. Cell Rep. 2015. PMID: 26686642 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of BAR Domain Proteins in the Regulation of Membrane Dynamics.Acta Naturae. 2016 Oct-Dec;8(4):60-69. Acta Naturae. 2016. PMID: 28050267 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma membrane topography governs the 3D dynamic localization of IgM B cell antigen receptor clusters.EMBO J. 2023 Feb 15;42(4):e112030. doi: 10.15252/embj.2022112030. Epub 2023 Jan 3. EMBO J. 2023. PMID: 36594262 Free PMC article.
-
The Tubulation Activity of a Fission Yeast F-BAR Protein Is Dispensable for Its Function in Cytokinesis.Cell Rep. 2016 Jan 26;14(3):534-546. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.12.062. Epub 2016 Jan 14. Cell Rep. 2016. PMID: 26776521 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Suetsugu S, Gautreau A. Synergistic BAR-NPF interactions in actin-driven membrane remodeling. Trends Cell Biol 2012; 22: 141–50; PMID:22306177; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2012.01.001 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Masuda M, Mochizuki N. Structural characteristics of BAR domain superfamily to sculpt the membrane. Semin Cell Dev Biol 2010; 21: 391–8; PMID:20083215; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2010.01.010 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Frost A, Perera R, Roux A, Spasov K, Destaing O, Egelman EH, De Camilli P, Unger VM. Structural basis of membrane invagination by F-BAR domains. Cell 2008; 132: 807–17; PMID:18329367; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.12.041 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carlson BR, Lloyd KE, Kruszewski A, Kim I-H, Rodriguiz RM, Heindel C, Faytell M, Dudek SM, Wetsel WC, Soderling SH. WRP/srGAP3 facilitates the initiation of spine development by an inverse F-BAR domain, and its loss impairs long-term memory. J Neurosci 2011; 31: 2447–60; PMID:21325512; http://dx.doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4433-10.2011 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Guerrier S, Coutinho-Budd J, Sassa T, Gresset A, Jordan NV, Chen K, Jin W-L, Frost A, Polleux F. The F-BAR Domain of srGAP2 Induces Membrane Protrusions Required for Neuronal Migration and Morphogenesis. Cell 2009; 138: 990–1004; PMID:19737524; http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.06.047 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
