Bacteriocin production augments niche competition by enterococci in the mammalian gastrointestinal tract
- PMID: 26479034
- PMCID: PMC4978352
- DOI: 10.1038/nature15524
Bacteriocin production augments niche competition by enterococci in the mammalian gastrointestinal tract
Abstract
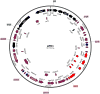
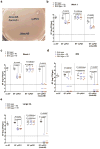
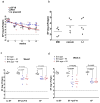
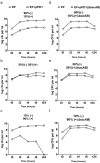
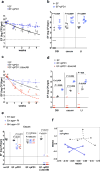
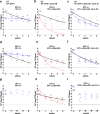
Enterococcus faecalis is both a common commensal of the human gastrointestinal tract and a leading cause of hospital-acquired infections. Systemic infections with multidrug-resistant enterococci occur subsequent to gastrointestinal colonization. Preventing colonization by multidrug-resistant E. faecalis could therefore be a valuable approach towards limiting infection. However, little is known about the mechanisms E. faecalis uses to colonize and compete for stable gastrointestinal niches. Pheromone-responsive conjugative plasmids encoding bacteriocins are common among enterococcal strains and could modulate niche competition among enterococci or between enterococci and the intestinal microbiota. We developed a model of colonization of the mouse gut with E. faecalis, without disrupting the microbiota, to evaluate the role of the conjugative plasmid pPD1 expressing bacteriocin 21 (ref. 4) in enterococcal colonization. Here we show that E. faecalis harbouring pPD1 replaces indigenous enterococci and outcompetes E. faecalis lacking pPD1. Furthermore, in the intestine, pPD1 is transferred to other E. faecalis strains by conjugation, enhancing their survival. Colonization with an E. faecalis strain carrying a conjugation-defective pPD1 mutant subsequently resulted in clearance of vancomycin-resistant enterococci, without plasmid transfer. Therefore, bacteriocin expression by commensal bacteria can influence niche competition in the gastrointestinal tract, and bacteriocins, delivered by commensals that occupy a precise intestinal bacterial niche, may be an effective therapeutic approach to specifically eliminate intestinal colonization by multidrug-resistant bacteria, without profound disruption of the indigenous microbiota.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
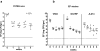






References
-
- Richards MJ, Edwards JR, Culver DH, Gaynes RP. Nosocomial infections in combined medical-surgical intensive care units in the United States. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2000;21(8):510–515. - PubMed
-
- Nes Ingolf F, D BD, Yasuyoshi Ike. Enterococcal Bacteriocins and Antimicrobial Proteins that Contribute to Niche Control BTI - Enterococci: From Commensals to Leading Causes of Drug Resistant Infection. In: Gilmore E-i-c Michael S, Clewell Don B, Ike Yasuyoshi, Shankar Nathan., editors. Enterococci: From Commensals to Leading Causes of Drug Resistant Infection. Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary; Boston: 2014. - PubMed
-
- Hooper LV, Midtvedt T, Gordon JI. How host-microbial interactions shape the nutrient environment of the mammalian intestine. Annu Rev Nutr. 2002;22(0199-9885):283–307. (Print) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- BioProject/PRJNA290480
- Actions
- SRA/SRP061808
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

