Mechanism of eIF6 release from the nascent 60S ribosomal subunit
- PMID: 26479198
- PMCID: PMC4871238
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.3112
Mechanism of eIF6 release from the nascent 60S ribosomal subunit
Abstract
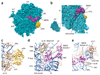
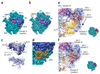
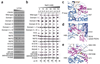
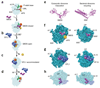
SBDS protein (deficient in the inherited leukemia-predisposition disorder Shwachman-Diamond syndrome) and the GTPase EFL1 (an EF-G homolog) activate nascent 60S ribosomal subunits for translation by catalyzing eviction of the antiassociation factor eIF6 from nascent 60S ribosomal subunits. However, the mechanism is completely unknown. Here, we present cryo-EM structures of human SBDS and SBDS-EFL1 bound to Dictyostelium discoideum 60S ribosomal subunits with and without endogenous eIF6. SBDS assesses the integrity of the peptidyl (P) site, bridging uL16 (mutated in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia) with uL11 at the P-stalk base and the sarcin-ricin loop. Upon EFL1 binding, SBDS is repositioned around helix 69, thus facilitating a conformational switch in EFL1 that displaces eIF6 by competing for an overlapping binding site on the 60S ribosomal subunit. Our data reveal the conserved mechanism of eIF6 release, which is corrupted in both inherited and sporadic leukemias.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Comment in
-
Ribosomal 60S-subunit production: the final scene.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2015 Nov;22(11):837-8. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.3121. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 26581515 No abstract available.
References
-
- Boocock GR, et al. Mutations in SBDS are associated with Shwachman-Diamond syndrome. Nat Genet. 2003;33:97–101. - PubMed
-
- Senger B, et al. The nucle(ol)ar Tif6p and Efl1p are required for a late cytoplasmic step of ribosome synthesis. Mol Cell. 2001;8:1363–1373. - PubMed
-
- Menne TF, et al. The Shwachman-Bodian-Diamond syndrome protein mediates translational activation of ribosomes in yeast. Nat Genet. 2007;39:486–495. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

