Effects of the phencyclidine model of schizophrenia and nicotine on total and categorized ultrasonic vocalizations in rats
- PMID: 26479849
- PMCID: PMC4834070
- DOI: 10.1097/FBP.0000000000000199
Effects of the phencyclidine model of schizophrenia and nicotine on total and categorized ultrasonic vocalizations in rats
Abstract
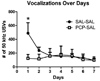
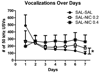
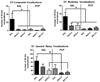
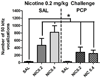
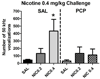
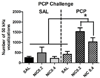
Patients with schizophrenia smoke cigarettes at a higher rate than the general population. We hypothesized that a factor in this comorbidity is sensitivity to the reinforcing and reinforcement-enhancement effects of nicotine. Phencyclidine (PCP) was used to model behavioral changes resembling negative symptoms of schizophrenia in rats. Ultrasonic vocalizations (USVs) in rats have been used to measure emotional states, with 50 kHz USVs indicating positive states and 22 kHz USVs indicating negative states. Total and categorized numbers of 22 and 50 kHz USVs and USVs during a visual stimulus (e.g. a potential measure of reinforcement-enhancement) were examined in rats following injection of PCP (2.0 mg/kg) and/or nicotine (0.2 or 0.4 mg/kg) daily for 7 days. PCP was then discontinued and all rats received nicotine (0.2 and 0.4 mg/kg) and PCP (2.0 mg/kg) on three challenge days. PCP acutely decreased 50 kHz vocalizations, whereas repeated nicotine potentiated rates of vocalizations, with similar patterns during light presentations. Rats in the PCP and nicotine combination groups made more 50 kHz vocalizations compared with rats in the control groups on challenge days. We conclude that PCP may produce a reward deficit, which is shown by decreased 50 kHz USVs, and behaviors post-PCP exposure may best model the comorbidity between schizophrenia and nicotine.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Abdul-Monim Z, Reynolds GP, Neill JC. The atypical antipsychotic ziprasidone, but not haloperidol, improves phencyclidine-induced cognitive deficits in a reversal learning task in the rat. Journal of Psychopharmacology. 2003;17(1):57–66. - PubMed
-
- Abdul-Monim Z, Neill JC, Reynolds GP. Sub-chronic psychotomimetic phencyclidine induces deficits in reversal learning and alterations in parvalbumin-immunoreactive expression in the rat. Journal of Psychopharmacology. 2007;21:198–205. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

