Non-Hematopoietic β-Arrestin1 Confers Protection Against Experimental Colitis
- PMID: 26479868
- PMCID: PMC4728047
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.25216
Non-Hematopoietic β-Arrestin1 Confers Protection Against Experimental Colitis
Abstract
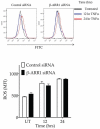
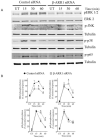
β-Arrestins are multifunctional scaffolding proteins that modulate G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR)-dependent and -independent cell signaling pathways in various types of cells. We recently demonstrated that β-arrestin1 (β-arr1) deficiency strikingly attenuates dextran sodium sulfate (DSS)-induced colitis in mice. Since DSS-induced colitis is in part dependent on gut epithelial injury, we examined the role of β-arr1 in intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) using a colon epithelial cell line, SW480 cells. Surprisingly, we found that knockdown of β-arr1 in SW480 cells enhanced epithelial cell death via a caspase-3-dependent process. To understand the in vivo relevance and potential cell type-specific role of β-arr1 in colitis development, we generated bone marrow chimeras with β-arr1 deficiency in either the hematopoietic or non-hematopoietic compartment. Reconstituted chimeric mice were then subjected to DSS-induced colitis. Similar to our previous findings, β-arr1 deficiency in the hematopoietic compartment protected mice from DSS-induced colitis. However, consistent with the role of β-arr1 in epithelial apoptosis in vitro, non-hematopoietic β-arr1 deficiency led to an exacerbated colitis phenotype. To further understand signaling mechanisms, we examined the effect of β-arr1 on TNF-α-mediated NFκB and MAPK pathways. Our results demonstrate that β-arr1 has a critical role in modulating ERK, JNK and p38 MAPK pathways mediated by TNF-α in IECs. Together, our results show that β-arr1-dependent signaling in hematopoietic and non-hematopoietic cells differentially regulates colitis pathogenesis and further demonstrates that β-arr1 in epithelial cells inhibits TNF-α-induced cell death pathways.
© 2015 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures



Similar articles
-
γ-Glutamyl cysteine and γ-glutamyl valine inhibit TNF-α signaling in intestinal epithelial cells and reduce inflammation in a mouse model of colitis via allosteric activation of the calcium-sensing receptor.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 May;1852(5):792-804. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2014.12.023. Epub 2015 Jan 3. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25558818
-
β-Arrestin-1 protects against endoplasmic reticulum stress/p53-upregulated modulator of apoptosis-mediated apoptosis via repressing p-p65/inducible nitric oxide synthase in portal hypertensive gastropathy.Free Radic Biol Med. 2015 Oct;87:69-83. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.06.004. Epub 2015 Jun 25. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015. PMID: 26119788
-
β-Arrestin-1 deficiency protects mice from experimental colitis.Am J Pathol. 2013 Apr;182(4):1114-23. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.12.025. Epub 2013 Feb 8. Am J Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23395087 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid xenograft tumor progression in beta-arrestin1 transgenic mice due to enhanced tumor angiogenesis.FASEB J. 2008 Feb;22(2):355-64. doi: 10.1096/fj.07-9046com. Epub 2007 Sep 21. FASEB J. 2008. PMID: 17890288
-
Targeting endothelin-1 receptor/β-arrestin1 network for the treatment of ovarian cancer.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2017 Oct;21(10):925-932. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2017.1361930. Epub 2017 Sep 5. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2017. PMID: 28758529 Review.
Cited by
-
β-arrestin1 protects intestinal tight junction through promoting mitofusin 2 transcription to drive parkin-dependent mitophagy in colitis.Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf). 2024 Sep 6;12:goae084. doi: 10.1093/gastro/goae084. eCollection 2024. Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf). 2024. PMID: 39246845 Free PMC article.
-
ARRB1 Drives Gallbladder Cancer Progression by Facilitating TAK1/MAPK Signaling Activation.J Cancer. 2021 Jan 30;12(7):1926-1935. doi: 10.7150/jca.53325. eCollection 2021. J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33753990 Free PMC article.
-
COX-1/PGE2/EP4 alleviates mucosal injury by upregulating β-arr1-mediated Akt signaling in colitis.Sci Rep. 2017 Apr 21;7(1):1055. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-01169-6. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28432343 Free PMC article.
-
Role of G protein-coupled receptor kinase-6 in Escherichia coli lung infection model in mice.Physiol Genomics. 2017 Nov 1;49(11):682-689. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00066.2017. Epub 2017 Sep 22. Physiol Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28939643 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA-miRNA-mRNA Network Analysis Reveals the Potential Biomarkers in Crohn's Disease Rats Treated with Herb-Partitioned Moxibustion.J Inflamm Res. 2022 Mar 5;15:1699-1716. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S351672. eCollection 2022. J Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 35282268 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Araki Y, Mukaisyo K, Sugihara H, Fujiyama Y, Hattori T. Increased apoptosis and decreased proliferation of colonic epithelium in dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice. Oncol Rep. 2010;24(4):869–874. - PubMed
-
- Babu D, Soenen SJ, Raemdonck K, Leclercq G, De Backer O, Motterlini R, Lefebvre RA. TNF-alpha/cycloheximide-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in murine intestinal epithelial MODE-K cells. Curr Pharm Des. 2012;18(28):4414–4425. - PubMed
-
- Begue B, Wajant H, Bambou JC, Dubuquoy L, Siegmund D, Beaulieu JF, Canioni D, Berrebi D, Brousse N, Desreumaux P, Schmitz J, Lentze MJ, Goulet O, Cerf-Bensussan N, Ruemmele FM. Implication of TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in inflammatory intestinal epithelial lesions. Gastroenterology. 2006;130(7):1962–1974. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

